Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
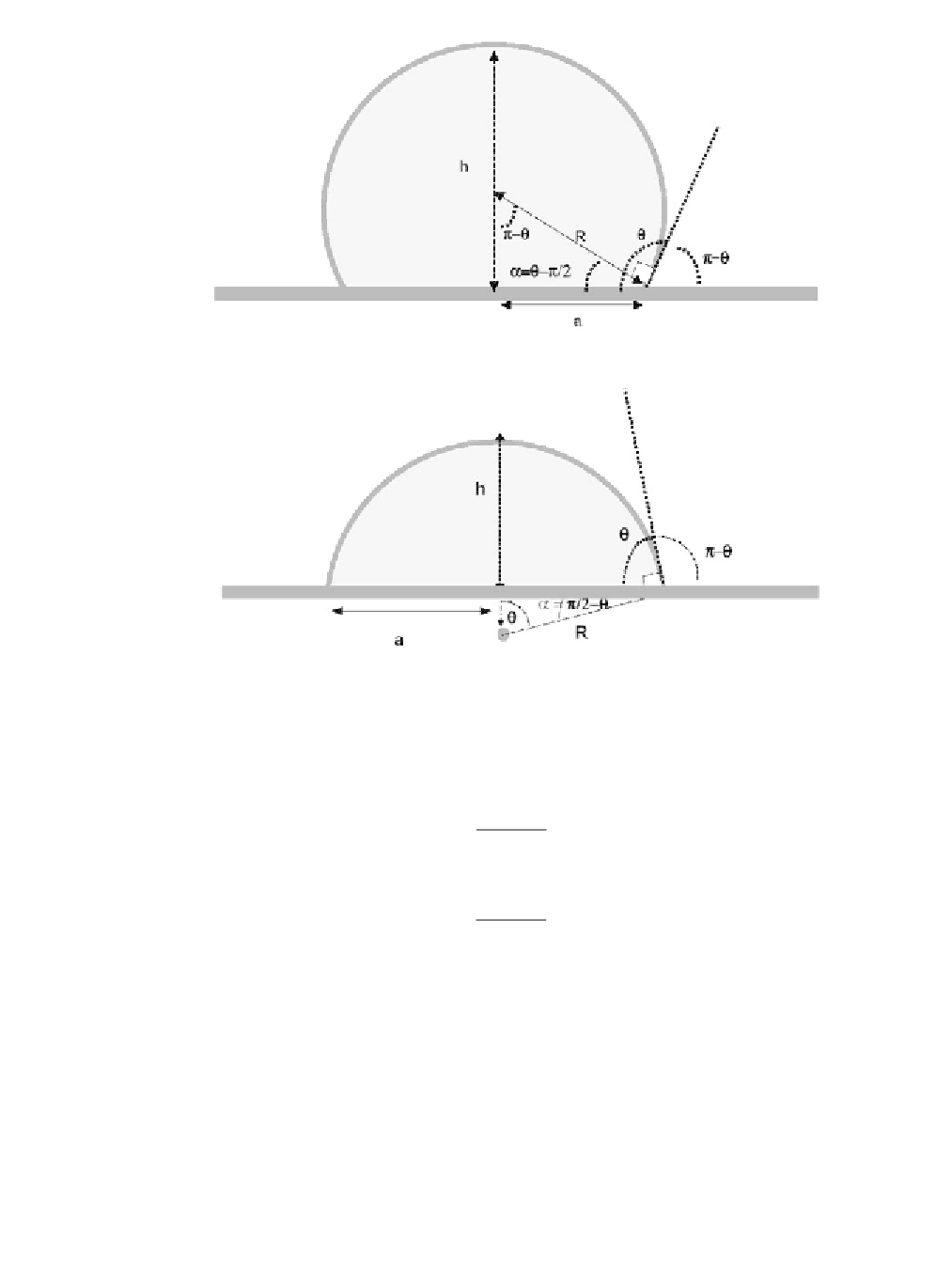
Figure 3.49
Cross section of a microdrop sufficiently small to be a spherical cap. (a) Nonwetting
droplet. (b) Wetting droplet. Notice that
a
=
q
-
π
/2 in the first (nonwetting) case and
a
=
π
/2
-
q
in the second (wetting) case.
Again, we shall not give the derivation of the surface area [8]. The usual expres-
sions are
2
2
π
h
S
( , )
θ
h
=
1 cos
-
θ
2
2
(3.75)
S a h
( , )
=
π
(
a
+
h
)
2
2
π
a
S a
( , )
θ
=
1 cos
+
θ
3.8.1.2 Droplets Constrained Between Two Plates
It happens very often in biotechnology that droplets are constrained between two
horizontal solid surfaces. Such droplets have a relatively smaller free energy than
sessile droplets and are easier to handle. This is particularly the case for electrowet-
ting. We consider here only the case of microsystems where the vertical gap
d
is
small (usually 50 to 500
m
m), their Bond number, given by
Bo
=
ρg
2
/
g
, is less than
0.1, and the free interfaces have circular cross sections.