Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
As an example, consider the AP CCateninT cf pathway for
human colon cancer. This is a multi-stage model involving the suppressor
genes in chromosomes 5q, 17p and 18q (see [29, 31, 35, 39, 47, 53, 10, 18]).
A schematic presentation of this pathway is given in Figure 1. This is only
one of the pathways for the colon cancer although it is the major pathway
which accounts for 80% of all colon cancers (see [29, 31, 35, 39, 47, 53, 10,
18]). In Figure 2, we present another multistage model for human colon
cancer involving mis-match repair genes (mostly hMLH1 and hMSH2) and
the Bax gene in chromosome 19q and the TGFR
I
I gene in chromosome
3p. This pathway accounts for about 15% of all human colon cancer.
The above example and studies in cancer biology
41
illustrate that car-
cinogenesis may involve a large number of cancer genes but only a few are
stage limiting genes whereas other cancer genes may be dispensed with al-
though these genes can enhance the cascade of carcinogenesis. As shown
by Renan
48
, it has been noted that while mutation of a single gene may
initiate the cascade of carcinogenesis in some cases such as retinoblastoma,
the process of carcinogenesis would usually involve 5 to 10 genes.
Second Copy
of hMSH2
(hMLH1)
Second Copy of
TGF
E
RII
Second Copy
of BAX
Ras
N
J
1
J
2
J
3
J
4
J
5
J
6
J
7
Myc
Mutation of
hMSH2 in
2p16
(or hMLH
1 in 3p21)
BAX in 19q13
E
-Catenin in 3p21
or other genes
TGF
E
RII in 3p22
Carcinomas
Fig. 2. The MSI-BAX-TGF RII Pathway of Human Colon Cancer. Here, N = Normal
stem cell, J
i
= The i
th
-stage initiated cell in the MSI pathway,#denotes mutation,
inactivation or loss of suppressor genes (hMSH2, hMLH1, BAX, TGF RII),&denotes
mutation or activation of oncogenes (Ras, Myc).

























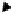


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search