Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
Upper Sideband Processing
f
Noncoherently
combination
Received
BOC signal
Lowpass Filter
I&D
Local
BPSK -R signal
e
j2
π
fst
Lower Sideband Processing
(Local signal is multiplied by
e
-j2
π
fst
)
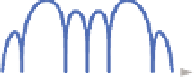
Fig. 7. Block diagram of BPSK-like method
Although the correlation functions in sideband techniques do not present any side peak,
meaning that they are fully unambiguous, this kind of methods suffers from some
drawbacks. The principle defect is that this kind of methods completely removes all of the
advantages of BOC signal tracking in terms of Gaussian noise and multipath mitigation,
since it causes the Gabor bandwidth of the received signal to approach that of the BPSK-R
signal. Moreover, two side lobes are combined in non-coherent mode, which introduces
correlation losses into the process. It seems that sideband techniques are not appropriate in
terms of tracking. However, the correlation functions in this kind of methods have wide
main correlation peak, which allows using longer code delay step in acquisition to reduce
mean acquisition time. Therefore, sideband techniques can be attractive options in BOC
modulated signal acquisition.
3.3 Time-domain unambiguous processing
Time-domain processing techniques are also referred to as side-peaks cancellation (SC)
techniques which solve the ambiguity problem by taking advantage of the geometrical
property of correlation functions (CF). The basic idea of SC techniques is using synthesized
correlation function (SCF) instead of BOC ACF in acquisition and tracking. CF between the
received BOC signal and some local auxiliary signals whose chip waveforms may be
different from the received one are combined linearly or non-linearly to form the SCF with
no side-peak. SC methods are flexible. Due to different auxiliary signal chip waveforms and
combination modes, SC methods differentiate from each other greatly.
The first side-peaks cancellation technique is proposed in (Ward, 2003). This approach
removes the ambiguities of the correlation function, but one drawback is that this method
destroys the sharp peak of the correlation function. For accurate tracking, preserving a sharp
peak of the correlation function is a prerequisite. An innovative unambiguous tracking
technique, which is referred to as autocorrelation side-peak cancellation technique
(ASPeCT), is described in (Julien et al., 2007). This technique uses ten correlation channels,
completely removing the side peaks from the correlation function and keeping the sharp





























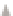

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search