Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
3.1 False lock detection & recovery
False lock detection and recovery technique does not remove ambiguity but rather checks
false lock. The most representative detection and recovery technique is referred to as bump-
jumping technique (Fine & Wilson, 1999). This technique employs the traditional ambiguous
code tracking loop and constantly check whether this loop is locked on the main peak of
BOC ACF. To do so, bump-jumping technique uses two additional correlators located at the
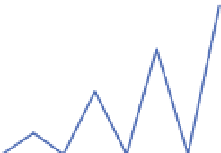
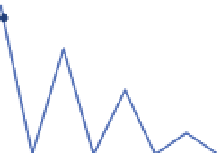
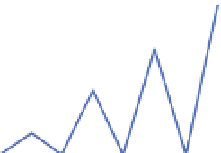
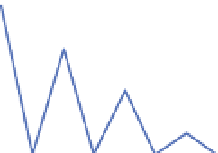
theoretical location of the two highest side peaks, as shown in Figure 5.
These two correlators are referred to as very early (VE) and very late (VL) correlators. By
measuring and comparing the magnitude of the outputs of these two correlators and the
prompt one, bump-jumping technique determines whether the false lock happens. It can be
seen from Figure 5 that ignoring the effect of noise, when the code loop locks on the main
peak, the magnitude of prompt correlator output is the greatest. And if either VE or VL
correlator output is the largest, it means that tracking might be biased, and the loop will
“jump“ in the appropriate direction.
When locked on the main peak, this technique has high tracking accuracy. However, since it
is based on the comparing of the main and side peaks magnitudes, the detection may have a
high probability of false alarm when the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is low. In (Fine &
Wilson, 1999), two up/down counter mechanisms are employed to reduce this false alarm
probability. After each comparison, if one of the magnitudes of VE and VL correlator
outputs exceeds that of the prompt one, the corresponding counter is incremented by one,
otherwise the corresponding counter is decremented by one. The counter is not
decremented below 0 or incremented above the preset threshold
N
. When the counter
reaches the threshold, the loop jumps to the highest peak. By using this counter mechanism,
the false alarm probability can be reduced effectively. However, the response time is also
increased. Once the false lock happen, this technique needs time to detect and recover from
false lock, so it might be intolerable for some critical applications such as aircraft landing.
P
VE
VL
EL
τ
|P|>|VE| & |P|>|VL|: lock on the main peak
VE
P
VL
EL
τ
|P|<|VE| or |P|<|VL|: lock on the side peak
Fig. 5. Bump-jumping technique

























Search WWH ::

Custom Search