Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
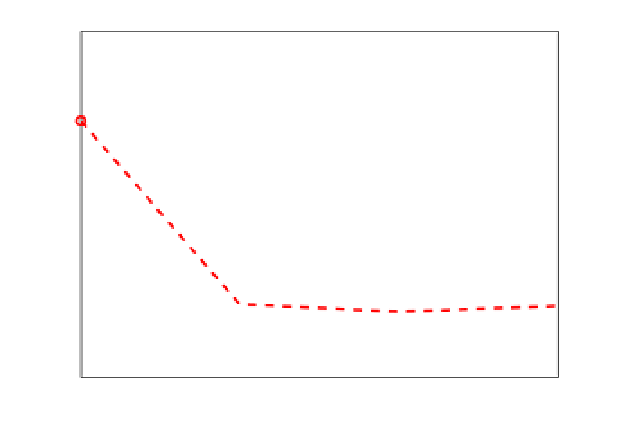
performance in this two to five paths closely spaced multipath channel. Among other
techniques, PT(Diff2) and HRC have better performance only in good C/N
0
(around 40 dB-Hz
and onwards). It can also be observed that the proposed SBME and TK+nEML do not bring
any advantage in the tracking performance as compared to nEML in this multipath fading
channel model. Here also, the SBME coefficient and the late slope were set to 0.007 and
−
4.5,
respectively.
CBOC(−) signal, 2 to 5 paths, BW 24.
552 MHz
70
nEML
HRC
TK+nEML
PT(Diff2)
SBME
RSSML
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
30
35
40
45
C/N
0
[dB−Hz]
Fig. 10. RMSE vs. C/N
0
plot for CBOC(-) modulated Galileo E1C signal in two to five path
Rayleigh fading channel.
7. Conclusion
This chapter addressed the challenges encountered by a GNSS signal due to multipath
propagation. A wide range of correlation-based multipath mitigation techniques were
discussed and the performance of some of these techniques were evaluated in terms of
running average error and root-mean-square error. Among the analyzed multipath mitigation
techniques, RSSML, in general, achieved the best multipath mitigation performance in
moderate-to-high C/N
0
scenarios (for example, 30 dB-Hz and onwards). The other
techniques, such as PT(Diff2) and HRC showed good multipath mitigation performance only
in high C/N
0
scenarios (for example, 40 dB-Hz and onwards). The other new technique
SBME offered slightly better multipath mitigation performance to the well-known nEML
DLL at the cost of an additional correlator. However, as the GNSS research area is fast
evolving with many potential applications, it remains a challenging topic for future research
to investigate the feasibility of these multipath mitigation techniques with the multitude
of signal modulations, spreading codes, and spectrum placements that are (or are to be)
proposed.
8. References
Baltersee, J., Fock, G. & Schulz-Rittich, P. (2001). Adaptive code-tracking receiver for
direct-sequence Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) communications over






































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search