Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
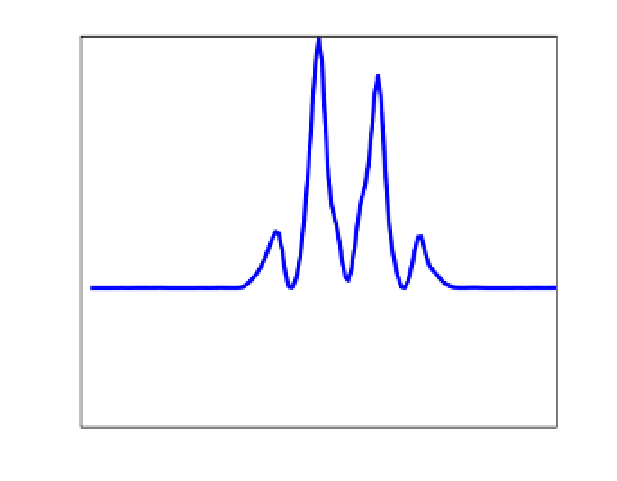
Two Path Nakagami−m fading channel, path delays: [0 0.75122] chips, C/N
o
:100dB−Hz
1
Correlation Function
Diff2
Diff2 Threshold
Noise Threshold
Competitive Peaks
0.5
0
−0.5
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
Delay Error [Chips]
Fig. 6. Generation of competitive peaks for PT(Diff2) technique.
Bhuiyan & Lohan (2010)) and is sensitive to the noise dependent threshold choice. Firstly,
it computes the noise variance, which is then used to compute an adaptive threshold. The
peaks which are above the adaptive threshold are considered as competitive peaks. Among
all the competitive peaks, TK selects the delay associated to that competitive peak which has
the closest delay difference from the previous delay estimate.
5.5 Reduced Search Space Maximum Likelihood delay estimator
A Reduced Search Space Maximum Likelihood (RSSML) delay estimator is another good
example of maximum likelihood based approach, which is capable of mitigating the multipath
effects reasonably well at the expense of increased complexity. The RSSML, proposed by
the Author in Bhuiyan et al. (2009) and then further enhanced in Bhuiyan & Lohan (2010),
attempts to compensate the multipath error contribution by performing a nonlinear curve fit
on the input correlation function which finds a perfect match from a set of ideal reference
correlation functions with certain amplitude(s), phase(s) and delay(s) of the multipath signal.
Conceptually, a conventional spread spectrum receiver does the same thing, but for only one
signal (i.e., the LOS signal). With the presence of multipath signal, RSSML tries to separate
the LOS component from the combined signal by estimating all the signal parameters in a
maximum likelihood sense, which consequently achieves the best curve fit on the received
input correlation function. As mentioned in Bhuiyan & Lohan (2010), it also incorporates
a threshold-based peak detection method, which eventually reduces the code delay search
space significantly. However, the downfall of RSSML is the memory requirement which it
uses to store the reference correlation functions.
In a multi-correlator based structure, the estimated LOS delay, theoretically, can be anywhere
within the code delay window range of
±τ
W
chips, though in practice, it is quite likely to have
a delay error around the previous delay estimate. The code delay window range essentially
depends on the number of correlators (i.e.,
M
) and the spacing between the correlators (i.e.,











































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search