Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
d
2
TEC
/
dβ
2
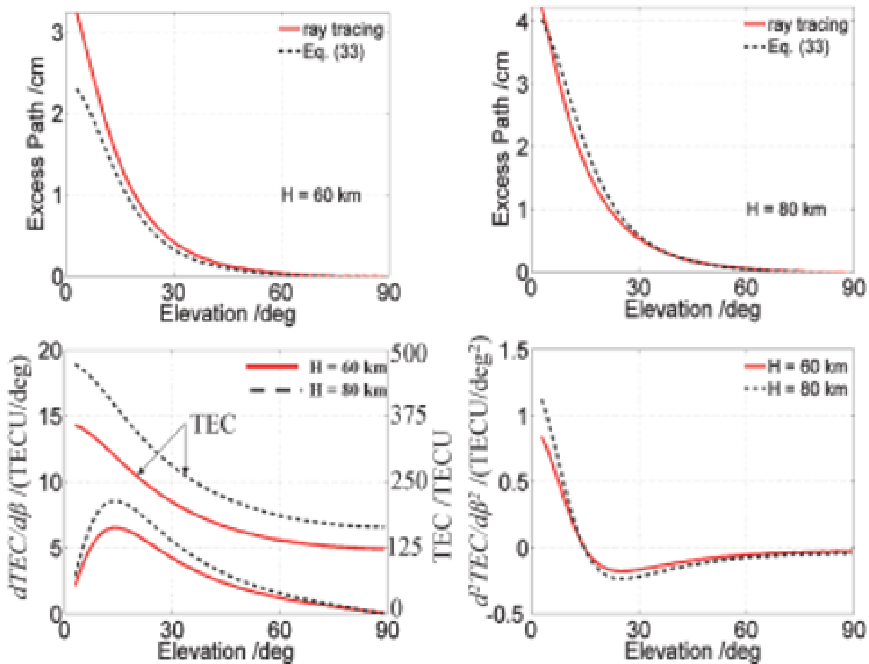
have been plotted as functions of elevation angle in Fig. 9. The
dTEC
/
dβ
has been
calculated dividing the TEC difference between two measurement epochs by the
corresponding elevation angle difference. Then,
d
2
TEC
/
dβ
2
has been calculated dividing the
dTEC
/
dβ
difference between two measurement epochs by the corresponding elevation angle
difference.
Comparing plots in Fig. 9, we see that although the dependency of
d
len
on the
dTEC
/
dβ
is not
straight forward, its dependency on the
d
2
TEC
/
dβ
2
is obvious at low elevation angles
(< 20°). Thus, the magnitude of the
d
len
depends on the magnitude of TEC as well as on the
magnitude of
d
2
TEC
/
dβ
2
. Considering this, functional dependencies have been studied
separately for different parameters to develop correction formulas. For this, ray tracing
calculation has been carried out for different geometrical and ionospheric conditions
varying elevation and Chapman layer parameters
H
,
Nm
and
hm
. Thus, the following
formula has been obtained for the
d
I
len
correction.
4
ray tracing
Eq. (33)
ray tracing
Eq. (33)
3
3
2
2
1
H = 60 km
1
H = 80 km
0
0
0 30 60 90
0 30 60 90
Elevation /deg
Elevation /deg
20
1.5
500
H = 60 km
H = 80 km
H = 60 km
H = 80 km
15
1
375
0.5
250
10
125
0
5
0
-0.5
0
0 30 60 90
0 30 60 90
Elevation /deg
Elevation /deg
Fig. 9. Elevation angle dependence of
d
I
len
, TEC (see right scale),
dTEC
/
dβ
and
d
2
TEC
/
dβ
2
for
the Chapman layer parameter
H
= 60 and 80 km
⎛
⎞
2
⎛
2
⎞
a
1
d TEC
⎜
⎟
len
I
2
(41)
1
d
=
−
1
TEC
+
⎜
a
cos
β
⎟
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎟
3
4
(
)
1/2
2
f
d
β
2
⎜
⎟
⎝
⎠
1c s
−
a
β
⎝
2
⎠








Search WWH ::

Custom Search