Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
5. External aiding acquisition technique for indoor positioning
In this section, a test-bed architecture, which is proposed by (Dovis et al., 2010), is introduced
as an example of the external-aiding acquisition approach.
5.1 Test-bed architecture
The test-bed as seen in Fig. 9 includes two chains:
Test receiver chain:
The main task of this chain is to collect a snapshot of the digitized GPS
signal and sends it to a location server through a cellular communication channel. The chain
consists of a GPS L1 front-end with the antenna at the test location. The RF front-end is
connected to a PC which collects digital sample streams into binary files. The local oscillator
is a rubidium (Rb) frequency standard (Datum8040, 1998) running the front-end through a
waveform synthesizer (HP, 1990).
Reference receiver chain:
The main task of this chain is to perform the HS acquisition
process taking advantage of the available assistance information. The chain consists of a
reference GPS receiver which processes open-sky signals from a fixed (known) location and
provides measurements to an assistance server. The latter provides the necessary aiding
information to the HS acquisition engine and the GPS Time indication for the synchronization
of the sample-stream recorder, performed before starting each signal collection session. The
synchronization process introduces an uncertainty on the GPS Time tags, since it is performed
by the software running at the PC, which is assumed to be 2s as in this work.
The assistance server is a software tool developed at Telecom Italia Laboratories to support
several test activities on Assisted GPS (A-GPS) technologies. It collects data from the reference
receiver and generates time-tagged log files with several kind of assistance information to be
provided to the HS acquisition engine. Each line of the log file, for each visible SV, contains
code-phase, Doppler frequency and Doppler rate estimates.
&('
$&'('
$#$&#(
$"')!!%
$#$&#(
$"')!!%
+
+
(a)
(b)
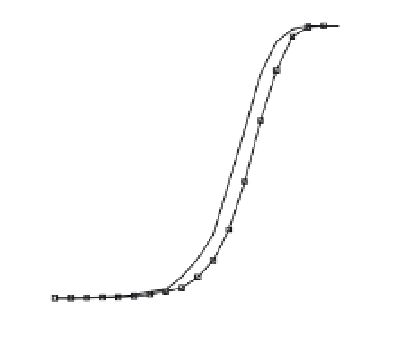
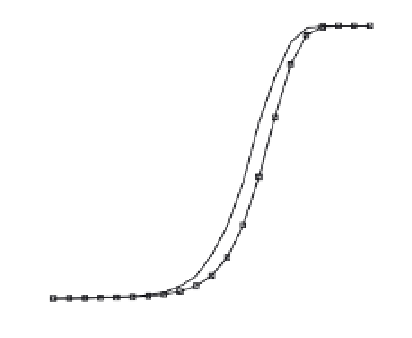
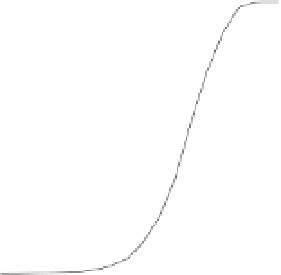
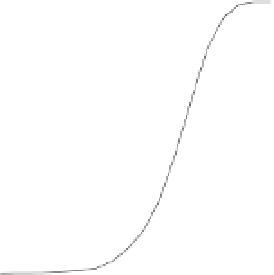
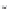
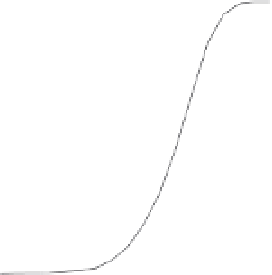
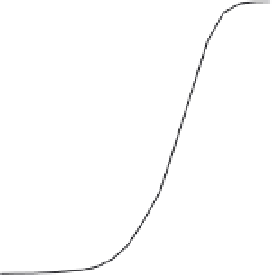
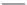
Fig. 8. Detection probability (
P
d
) of all post-correlation processing techniques at different
signal power levels in (a) perfect case:
f
d
=
f
d
=
0 Hz; (b) worst case:
12.5 Hz for
f
d
=
coherent combination (i.e. full 20-ms acquisition) and
250 Hz for the other techniques.


































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search