Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
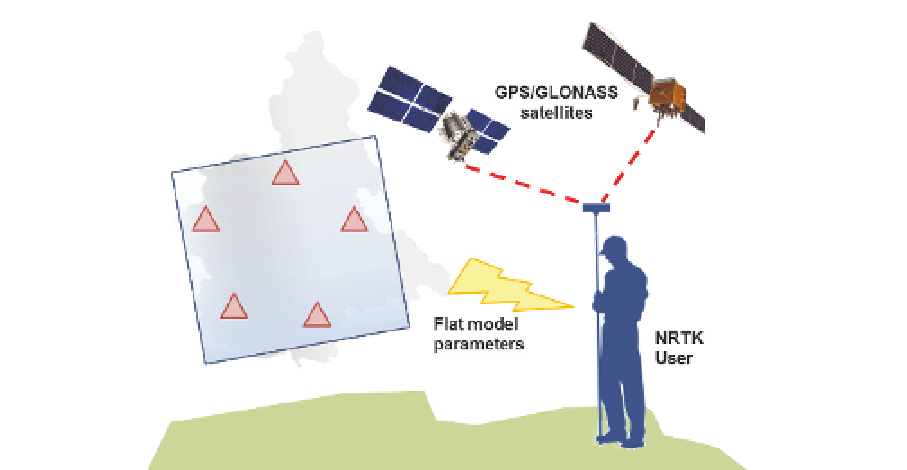
Fig. 2. The FKP positioning concept
The application of the positioning strategy is very simple. Four parameters, named
E
0
,
N
0
,
E
1
,
N
1
can be computed considering the estimated values of geometric and ionospheric
delays, using a given reference position (ϕ
R
, λ
R
). After that, it is possible to calculate the
terms:
(
(
)
(
)
)
δ
r
=
6.37
N
ϕ ϕ
−
+
E
λ λ
−
cos
ϕ
0
0
R
0
R
R
(8)
(
)
(
)
(
)
δ
r
=
6.37
H N
ϕϕ
−
+
E
λλ ϕ
−
cos
I
1
R
1
R
R
where:
)
3
(
H
=+
1160.53
−
E
π
/
(9)
where
E
is the satellite elevation (in radians). Finally, the two carrier-phase corrections (in
meters) are:
(
)
δ
r
=+
=+
δ
r
60 / 77
77 / 60
δ
r
f
1
0
I
(10)
(
)
δ
r
δ
r
δ
r
f
2
0
I
4.3 The MAC positioning
In 2001, Euler et al. (2001) had proposed a new approach to the use and transmission of
network corrections called Master Auxiliary Concept (MAC). The concept is the same as
above: a common level of network ambiguity fixing is estimated and the corrections are
transmitted to the rover separating dispersive and non-dispersive components.
In the MAC positioning, the coordinates and the biases of a single reference station (master
station) are broadcasted to the rover in addition to the single differences (both corrections
and coordinates) of the other stations in the network (auxiliary stations).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search