Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
- BPSK(
f
c
):
+
∞
∑
(
)=
q
k
Π(
−
)
c
t
t
kT
c
(2)
k
=
−
∞
where
is the rectangular function;
q
k
is the PRN code. Because of the properties of the PRN
code,
q
k
is a periodic sequence with the period
N
chips,
q
k
can be rewriten as
q
k
=
Π
q
mod
(
k
,
N
)
,
then the digital version of (2) is
+∞
∑
c
[
n
]=
c
(
nT
S
)=
q
mod
(
k
,
N
)
Π
(
nT
S
−
kT
c
)
(3)
k
=
−
∞
being
T
c
, and
f
c
=
1/
T
c
the chip duration (s) and chipping rate (chip per second - cps)
respectively.
- BOC(
f
s
,
f
c
): Similarly,
∞
∑
[
]=
s
mod
(
k
,
a
/2
)
Π (
−
)
c
n
q
mod
(
k
,
N
)
n
kT
c
(4)
=
−
∞
k
2
f
s
with
s
mod
(
k
,
a
/2
)
∈{−
}
=
f
c
. Usually in
GNSS
f
s
is a multiple of
f
c
(i.e.
a
/2 is an integer value) and both the values of
f
c
and
f
s
are
normalized by 1.023 MHz; for instance BPSK(5) and BOC(10,5) mean
f
c
1, 1
is the sub-carrier with the frequency
f
s
and
a
=
×
5
1.023 MHz and
f
s
=
10
×
1.023 MHz. The subcarrier
s
[
n
]
can be sine-phased,
s
[
n
]=
sgn
[
sin
(
2
π
f
s
nT
S
)]
;or
cosine-phased,
s
[
n
]=
sgn
[
cos
(
2
π
f
s
nT
S
)]
with sgn
(
x
)
being the signum function of
x
.
2.2 Conventional acquisition process
As introduced in (Kaplan, 2005), the conventional acquisition process (see Fig. 1) strives
to determine the presence of a desired signal defined by PRN code (
c
), code delay (
τ
) and
Doppler offset (
f
D
) in the incoming signal. The uncertainty regions of
(
c
,
τ
,
f
D
)
form a signal
,
f
D
(
c
,
ˆ
)
search-space, each cell
τ
of which is used to locally generate an equivalent tentative
[
]
signal, see Fig.
2(a).
The acquisition process correlates the incoming signal (
r
n
) with the
tentative signal (
r
[
n
]
) to measure the similarity between the two signals.
r
[]
S
R
1
L
()
m
⋅
L
n
=
1
{
}
(
)
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
exp
j
2
π
f
+
f
nT
cn
τ
[
+
]
IF
D
S
Fig. 1. Conventional signal acquisition architecture
It is well known that there are several general approaches to code acquisition of a GNSS
signals. The basic functional operation is a correlation between a local replica of the code and
the incoming signal as depicted in Fig. 1, where a serial approach scheme is reported. Time





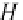























Search WWH ::

Custom Search