Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
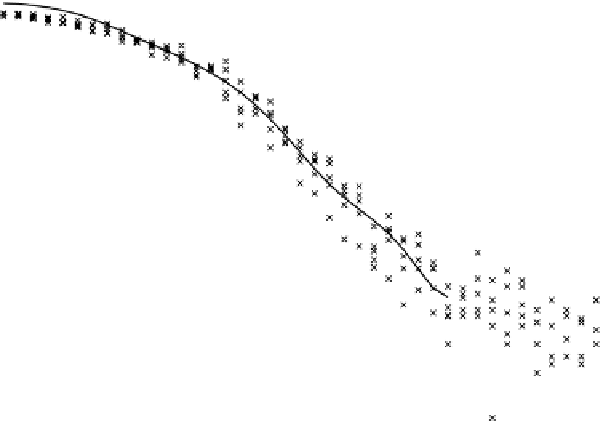
Bit error rate vs. signal−to−noise ratio — UMTS Case 4
10
0
Rake−4 Receiver Performance (Montium)
Average Rake−4 Receiver Performance (Montium)
Rake−4 Receiver Performance (Reference)
Average Rake−4 Receiver Performance (Reference)
10
−1
10
−2
10
−3
10
−4
−20
−15
−10
−5
0
5
10
15
20
E
c
/N
0
[dB]
FIgure 15.8
The BER before error correction of the Rake-4 receiver under case 4 propagation
conditions with ideal channel estimation (+ and × indicate individual simulation points).
utilizes multiple subcarriers within a single channel. The modulation technique divides
the high-data-rate information into several parallel bit streams, and each of these bit
streams modulates a separate subcarrier.
OFDM-based communication systems are all designed according to a generic frame-
work.
Figure 15.10
shows the generic OFDM framework of an OFDM receiver. In this
framework the characteristic properties are based on specific OFDM standards. This
means that, for example, the number of subcarriers and the length of the guard interval
may differ for different OFDM standards. The characteristics of an OFDM receiver for
a single standard can even differ in the case where it has different modes defined. Char-
acteristics of some OFDM-based standards, HiperLAN/2, DAB, and DRM are summa-
rized in
Table 15.6
[13-15].
15.3.1.4 OFDM Case Study: HiperLAN/2 Receiver Implementation
Parts of the baseband processing of a HiperLAN/2 receiver are implemented in the het-
erogeneous reconfigurable SoC of
Figure 15.3
. The coarse-grained Montium architecture
[26, 28] is used as the target architecture for mapping the baseband DSP algorithms. The
physical layer of the HiperLAN/2 receiver [13] is implemented on Montiums in combi-
nation with a GPP.
Figure 15.11
shows the baseband processing blocks of the receiver
that are implemented in the SoC. The solid arrows in Figure 15.11 indicate the data,
which is processed in consecutive processing tiles. The input consists of data samples,


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search