Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
10
0
MC−ISR without CFOR
MC−ISR with CFOR
MC−ISR with CFO = 0 Hz
10
−1
5
%
10
−2
10
−3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SNR in dB
BER versus SNR for MT-CDMA MC-ISR,
L
= 96,
N
c
= 7,
C
= 5,
with and with-
FIgure 10.4
out CFOR.
correlated across subcarriers and varying in time with Doppler shift
f
D
. We suppose a
low Doppler situation
f
D
= 8.8 Hz unless otherwise mentioned. We consider that time
delays vary linearly in time with a delay drift of 0.049 ppm. The receiver has
M
= 2 anten-
nas. We implement closed-loop power control operating at 1,600 Hz and adjusting the
power in steps of ±0.25 dB. An error rate on the power control bit of 5% and a feedback
delay of 0.625 ms are simulated. The simulation parameters common to all multicarrier
system configurations are listed in
Table 10.2
.
Table 10.3
shows the parameters specific to each multicarrier CDMA configuration.
We choose as a reference the 3G DS-CDMA (
N
c
= 1) system with spreading factor
L
= 32
and a chip rate of 3.84 Mcps. We assume frequency-selective fading with
P
= 3 propaga-
tion paths. One of the features of MT-CDMA is that for a constant bandwidth the ratio
between the spreading factor
L
and 2
K
=
N
c
- 1 is constant. We hence maintain the same
chip rate (3.840 Mcps) by changing the spreading factor and the number of subcarriers,
as shown in
Figure 10.3
. We consider four MT-CDMA configurations. Since they use
the same chip rate, there are three paths in each MT-CDMA subcarrier. For a fair com-
parison among different configurations of MC-DS-CDMA, the bandwidth should be the
same. By reducing the chip rate, we varied the number of subcarriers while maintaining
the orthogonality between them, as illustrated in Figure 10.3. Due to the reduction in
bandwidth, each subcarrier in MC-DS-CDMA has either two paths (i.e.,
P
= 2) or one
path (i.e.,
P
= 1, frequency-non-selective fading) for
N
c
= 3 and
N
c
≥ 5, respectively. The
main performance criterion is the link-level SNR required per carrier to meet a BER of
5% in order to achieve a QoS of BER = 10
-6
after channel decoding and the resulting
system-level throughput. The user's data rate is calculated by summing the data rates
over all subcarriers.


















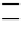
Search WWH ::

Custom Search