Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
c
u
n
(
t
)
e
j
2
πf−K
t
b
u
−K,n
c
u
n
(
t
)
e
j
2
πfK
t
b
u
K,n
s
u
(
t
)
Data
Σ
RF
conversion
c
u
n
(
t
)
e
j
2
πfK
t
b
u
K,n
IDFT
Power
control
Imput from
other users
Interference
construction
Rx 1
b
u
−K,n
b
u
K,n
Rx 2
Y
n
Pre−
processing
BB
conversion
b
u
K,n
Channel
identifi-
cation
synchron-
ization
Rx M
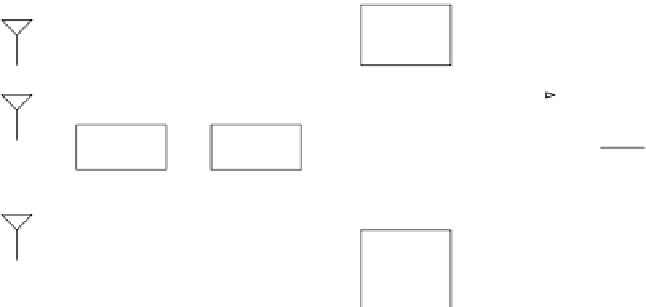
FIgure 10.2
Block diagram of the MC-CDMA transmitter and receiver (pulse shape filtering
is implemented at both transceiver ends).
hence eliminate the guard interval. Finally, the signal is transmitted after radio fre-
quency upconversion.
The modulated subcarriers are orthogonal over the symbol duration
T
MC
. The fre-
quency corresponding to the
k
t h
subcarrier is
f
k
= λ ×
k
/
T
MC
. The transmitter belongs to
the family of MT-CDMA if λ is set to 1, and to the class of MC-DS-CDMA if λ is set to
L
(see resulting signal spectra in
Figure 10.3
). Indeed, in an MT-CDMA system, the sub-
carrier frequencies are chosen to be orthogonal harmonics with minimum frequency
separation before spreading. By contrast, in MC-DS-CDMA, the subcarrier frequen-
cies are chosen to satisfy the orthogonality condition with minimum possible frequency
after spreading. The transmitted signal of the
u
th
user is given by





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search