Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
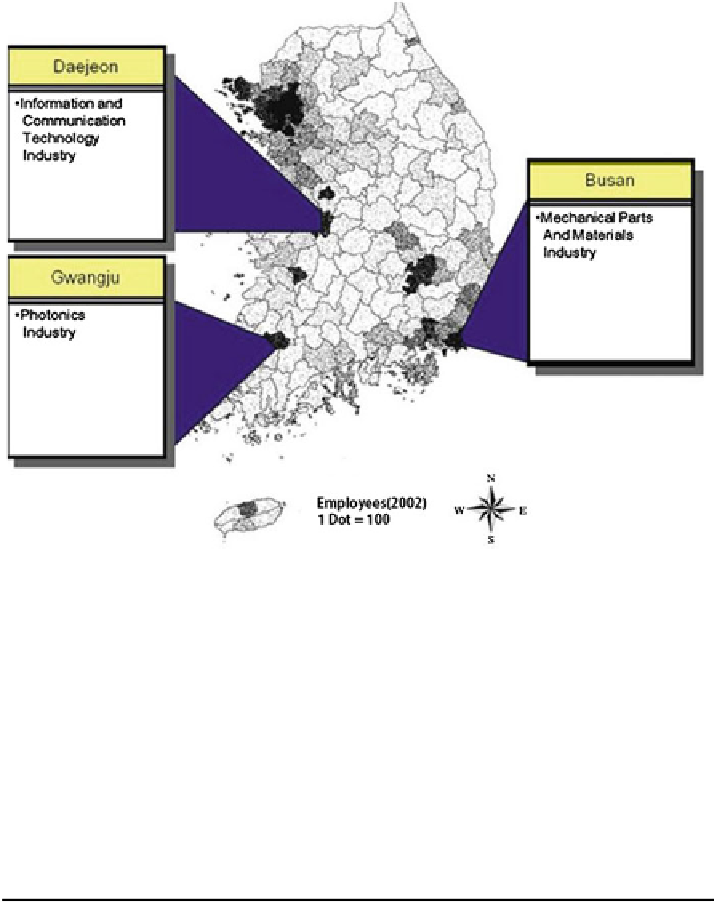
Fig. 1
Major strategic industries in three large cities. source (Kwon et al.
2005
)
Table 1 Characteristics of the sample (percentages)
Characteristics
Busan
Gwangju
Daejeon
Total sample
(a) Year firms started
(N = 60)
(N = 29)
(N = 56)
(N = 145)
Before foreign currency crisis
43(71.7)
3(10.3)
15(25.0)
61(42.1)
1998-2000
5(8.3)
13(44.8)
35(58.3)
53(36.5)
After 2001
12(20.0)
13(44.8)
6(10.0)
31(21.4)
(b) Size of firms
(N = 60)
(N = 57)
(N = 59)
(N = 176)
Micro \ 20 employees
9(15.0)
39(68.4)
30(50.8)
78(44.3)
Small 21-100
38(63.4)
16(28.0)
27(45.8)
81(46.0)
Medium 101-300
8(13.3)
1(1.8)
2(3.4)
11(6.3)
Large [ 300 employees
5(8.3)
1(1.8)
0(0.0)
6(3.4)
Source: (Kwon et al.
2005
) survey results
Gwangju, companies that were set up after 2001 were surveyed the most. This is
reflected on the size of the companies. In Gwangju and Daejeon, the proportion of
small-sized enterprises is higher than the average while in Busan those of small
and medium-sized, and large enterprises are high.
Despite that, in the mechanical parts and materials industry of Busan, most of the
companies are small and medium-sized with large ones taking only 8 %. These
companies were established before 1997. The oldest company of those surveyed


Search WWH ::

Custom Search