Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
controlled through thermodynamic and nonthermodynamic processing variables, e.
g., synthesis temperature, additives, and stirring speed. Hydrothermal synthesis
yielded well-crystallized needle-like HAp powders (size range 20
300 nm) with
minimal levels of aggregation. The thermodynamic model appears to be applicable
for both stoichiometric and nonstoichiometric compositions. Experimental condi-
tions for hydrothermal synthesis of HAp were based upon calculated phase bound-
aries in the system CaO
H
2
O between 25
C and 200
C. Phase
diagrams were calculated at each experimental temperature using commercial ther-
mochemical process simulation software. Briefly, standard state chemical potentials
at the temperature of interest are calculated either from temperature-dependent
equilibrium constant functions for each species. The standard state heat capacities
were both used in conjunction with solute and solvent activity coefficients. The
equations used to calculate the latter quantities were documented by Lencka and
Riman
[171]
. The standard state quantities
P
2
O
5
NH
4
NO
3
G
f
; Δ
H
f
;
S
f
Þ
for the solute species
were generally taken from the standard references and data bank
[167
ðΔ
171]
.
Changes in solute-free energies were calculated as functions of temperature and
pressure using the modified HKF model.
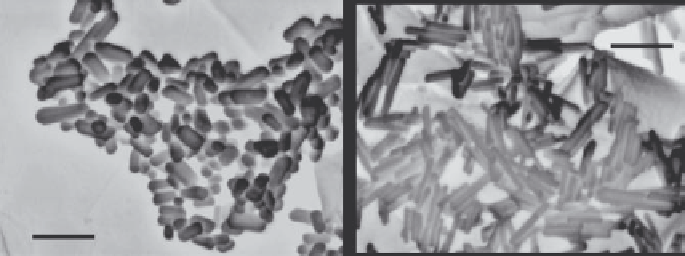
Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) photographs of selected
batches of HAp crystals synthesized at 200
C in 1 wt% KCl (aq.) and 50 vol.% 2-
propanol (aq.) are shown in
Figure 10.55
. HAp crystals synthesized in 50 vol.% 2-
propanol (aq.) had low aspect ratios ranging between 2 and 3 and diameters between
20 and 40 nm
Figure 10.55a
. Conversely, uniform nanosized needles (dimensions of
about 20
8) (
Figure 10.55b
)wereformedwhen
1 wt% KCl additive was used. HAp crystals prepared under similar conditions but
without additives were
100
160 nm, aspect ratio of 5
3
100 nm in size, yielding aspect ratios between 3
and 5. Here, the authors explain the possible mechanism of the morphology control
for HAp
[28,272]
.
Formation of amorphous calcium phosphates Acepromazine (ACP) prior to
hydrothermal reaction may explain why either equiaxed nanoparticles or anisotro-
pic needles, over the range of experimental conditions, are formed. Since ACP has
20
50
B
3
(a)
(b)
200
nm
200
nm
Figure 10.55 HAp crystals prepared hydrothermally at 200
C for 24 h using moderate
stirring. Room temperature pH of precursor slurries was 10. (a) Powders crystallized in
50 vol% 2-propanol in H
2
O (aq.) and (b) powders crystallized with 1 wt% KCl (aq.).