Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Surfactant
+
additive
+
dopant
Starting
materials
(TiO
2
/ZnO)
Suitable
solvent
NaOH and HCL
The starting
materials
mixture is
thoroughly
mixed in liner
Sample
preparation
Teflon liner inserted into autoclave
Treated in a desired
temperature and for
a desired duration
Hydrothermal treatment
Autoclave is cooled to the room temperature
after the experiment run
Product
cleansing
Rinsing with alkali/acid then with distilled water
Centrifugation/ultrasonication
Dried in freeze-drier
Desired final products
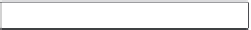
Figure 10.27 Flow chart of the experimental methodology adopted in the synthesis of TiO
2
and ZnO nanoparticles.
available in the literature. Several surface modifiers like n-butylamine, caprylic acid,
oleic acid, gluconic acid, benzylaldehyde, olcylamine, sodium dodecyl sulfate, citric
acid, triton-X, and n-hexanol were used. A major disadvantage in using some surfac-
tants, which mask the properties of the inorganic core material and also when used in
surplus, can produce in some cases thick and nonuniform outer coatings, leading to
the loss of desired properties of the inorganic core material.
Doping
An important part of the crystallization process whether it is the growth of bulk
materials or nanomaterials, dopants play an important role in controlling the crys-
tallization processes to some extent, particularly in controlling the morphology, as
they hinder growth along some directions in the crystal. There have been several
explanations put forward to explain doping difficulties in wide band gap semicon-
ductors
[123,124]
. First, there can be compensation by native point defects or