Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
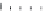
Figure 8.11 Variation of the
inverse magnetic susceptibility
Xg
2
1
with temperature
[33]
.
CO
2
FPO
4
Mn
2
FPO
4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
θ
p
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
T
(K)
transitional metals are the common ones. Tungstates are either simple or mixed
types but exhibit high thermal and chemical stability in general. The important
physical properties are excellent luminescent and electrical conductivity.
Tungstates can be obtained by different methods, like solid-state reactions, flux,
and hydrothermal; however, it is the flux method that is very popular in the growth
of a large variety of tungstates. With the recent advances in the hydrothermal
chemistry of various inorganic systems and the influence of organic precursors or
solvents in the growth of various inorganic compounds, the hydrothermal synthesis
of tungstates is becoming popular. Several simple and complex tungstates, like
Me
2
1
WO
4
(Me
Ca, Cd, Mn, Fe, Ca, Sr, Ba, Cd, Mn, Zn), M
2
2
M(WO
4
)
2
, MLn
5
(WO
4
)
2
(M
rare earths), have been reported. In general, the
synthesis of Sr and Ba tungstates are carried out using either an (NaOH) solution
or chloride solution, whereas it is only possible to obtain growth of Ca, Cd, Mn
and Fe, in the chloride solutions with 100% output
[40
Li, Na, K, Rb; Ln
5
5
42]
. Wolframites of diva-
lent metals belong to two structural groups, one crystallizing in the scheelite type
covering CaWO
4
, SrWO
4
, and BaWO
4
; the second one crystallizing in the wol-
framite structure type covering CdWO
4
, MnWO
4
, and FeWO
4
. The first group usu-
ally forms bipyramidal crystals of 3
5 mm size. The second group of crystals are
usually prismatic in form and their synthesis is carried out from a mixture of
M
2
1
O and WO
3
(M
2
1
5
550
C and
pressure up to 2000 atm. As mineralizers, aqueous solutions of chlorides and more
Cd, Mn, Fe) in 1:1 ratio at temperature 375