Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Hydrothermal Research
in Materials Science
(a)
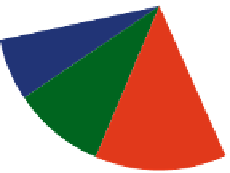
Canada 2%
Others
10%
India 3%
USA
23%
Taiwan 3%
UK 4%
Germany
6%
France
6%
Japan
20%
CIS
9%
Based upon analysis of 2601
papers from CAS, SCI, and
INSPEC databases in 1989-1997
China
13%
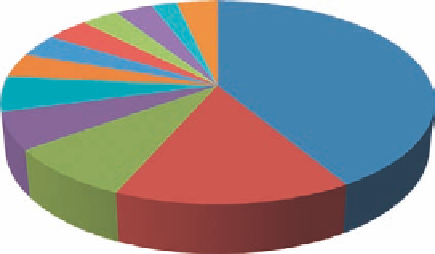
4%
(b)
3%
2%
3%
Germ
any 6%
USA
15%
Figure 1.14 (a) Number of papers on Hydrothermal Research in Materials Science country-
wise during 1989
1999. (b) Number of papers on Hydrothermal Research in Materials
Science country-wise during 2000
mid-2011.
greatly to understanding of the hydrothermal technique. One can now understand
the hydrothermal chemistry of solutions more or less precisely, which provides a
solid base for hydrothermal synthesis and processing at much lower pressure and
lower temperature conditions
[12,35]
. These developments are slowly removing the
concept of the black box for the hydrothermal system, and one can make use of
thick-walled silica autoclaves to carry out hydrothermal experiments up to a tem-
perature of 300
C and pressure up to several hundreds of bars, to facilitate direct
observation of the hydrothermal processes taking place in a given system. Already
some groups in Russia, Japan, and the United States have begun work in this direc-
tion and numerous publications have appeared. These developments have given
the hydrothermal technique an edge over other techniques for the preparation of
pure materials as it is a closed system providing a more controlled diffusion.