Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
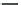
Table 7.13 New Silicates of Zirconium
[95]
Compound
Unit Cell Parameters
Space Group
a
(
˚
)
b
(
˚
)
c
(
˚
)
Na
8
ZrSi
6
O
18
7.371
R3m
α
5
88.34
Na
8
SnSi
6
O
18
7.344
R3m
α
5
87.82
Na
3
HZrSi
2
O
8
9.036
6.953
5.558
12/m
87.74
α
5
β
5
89.75
γ
5
89.16
Zircinalite N
4
ZS
6
Elpidite
NZS
6
3H
Catapleite
NZS
3
2H
Synthetic
N
2
Z
2
C
5
H
Synthetic
N
2
Z
2
C
2
H
4
Synthetic
N
2
Z
2
S
3
Zircon
ZS
Vlasovite
NZS
4
Ilerite
N
2
Z
2
S
6
6H
Synthetic
NZS
Geidonneite
N
2
Z
2
S
6
6H
Parakeldyshite
NZS
2
denotes the transitions with the temperature rise.
denotes paragenesis, dashed lines denotes natural paragenesis,
N = Na
2
O, Z = ZrO
2
, S = SiO
2
and H = H
2
O.
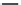
Figure 7.22 Scheme of zirconium silicate crystallization
[95]
.
crystal phases. With an increase in the NaOH concentration, the process of the for-
mation of alkali-zirconium silicates proceeds with the depolymerization of the
Si
a
O radicals: infinite [Si
6
O
15
] chains in elpidite
.
infinite [Si
4
O
11
] chains in vla-
sovite
.
island [Si
3
O
9
]
rings
in catapleite
.
[Si
2
O
7
] diorthogroups
in para-
keldyshite
[SiO
4
] orthogroups in the synthetic Na
4
Zr
2
Si
5
O
16
and Na
3
HZrSi
2
O
8
phases. Barth et al.
.
[101]
studied the structure and ionic conduction in