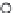Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 7.3 Decrease in the tilt
angles between tetrahedral
[7]
.
Conc. Ge (at%)
100
a
P
(Kbar)
80
61.4
55.8
60
48.6
37.6
40
20.7
20
0
-16
-20
-25
Table 7.4 Comparison of Structural Parameters in Quartz Under High Pressure
with the Substitution of Si for Ge
[7]
Pressure
Substitution of Si for Ge
Structural Parameter
1 bar
61.4 kbar
(Si
0.86
Ge
0.14
)
GeO
2
+
T
a
O
a
T
143.73
134.2
142.2
130.1
Intertetrahedral
3.331
2.925
3.304
3.024
Distances O
a
O
˚
3.411
3.064
3.406
3.193
Tilt angle
2
16.37
2
23.47
2
17.41
2
26.55
(O
a
T
a
O)-angle's dispersion
0.67
5.51
1.04
10.09
discuss the silicate structure, followed by phosphates, borates, vanadates, sulfates,
etc., with reference to their properties. Only some representative compounds have
been discussed covering all the tetrahedrally coordinated compounds.
In principle, there are several ways to search new crystalline phases under hy-
drothermal conditions:
The investigation of phase diagrams of crystallization for complicated systems and of
hydrothermal chemistry of individual elements.
The direct search for new compounds with the preset physical properties.
The study of hydrothermal reactions under new pressure
temperature conditions.
The modification of known compounds with the help of isomorphic displacements or of
special doping.
The above aspects have been discussed, in this topic, for silicates, germanates,
phosphates, borates, arsenates, vanadates, molybdates, tungstates, fluorides, etc.