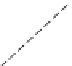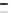Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
υ
(mm/day)
[100]
[111]
υ
´
(mm/day)
1.0
[111]
[100]
0.20
0.5
0.10
[110]
[110]
0
10
20
30
Δ
T (°C)
0
10
20
30
Δ
T (°C)
(a)
(b)
υ
´
(mm/day)
3
[100]
υ
(mm/day)
[111]
[100]
5
[111]
2
3
1
[110]
1
[110]
0
10
20
30
0
10
20
(c)
T (°C)
(d)
Δ
T (°C)
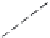
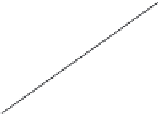
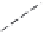
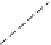
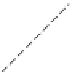
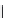
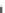
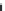
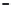
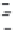
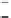
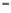
Figure 6.26 Relation between the growth rates of sodalite crystals
[122]
.
aluminosilicate zeolites and form a part of the history of framework of oxide
molecular sieves. The basis for the synthesis of such zeolites is the crystal chemical
similarities between Si and P, and AlPO
4
and SiO
2
in particular. The unique feature
of these zeolites is the compositional similarity and a great structural diversity. The
basic structural units consist of alternating Al and P with Al exhibiting octahedral
coordination and pressure and tetrahedral coordination. The two waters of hydra-
tion occupy positions in the coordination sphere of Al.
The synthesis of aluminophosphate zeolites does not differ much from that of the
synthesis of aluminosilicate zeolites, and the procedure is as follows: Equimolar
amounts of a reactive hydrated alumina, like boehmite, and phosphoric acid are
dissolved in water. An aluminophosphate gel is formed to which a templating agent
(R), an organic amine or a quaternary ammonium salt is added. This mixture is
digested quiescently in the preferred temperature range of 125
200
C. A crystalliza-
tion product is formed, which is worked up using procedures typical of zeolite
synthesis. About 23 structure analogues of three zeolites namely erionite (AlPO
4
-17),
sodalite (AlPO
4
-20), and analcime (AlPO
4
-24) have been obtained
[129]
. Some of
the novel structures are AlPO
4
-5, -11, -14, -18, -31, and -33. Among these, AlPO
4
-5