Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 6.5 Building Units in Zeolite Structures
[27]
Primary Building Units
(PBUs)
Tetrahedra (TO
4
)
Tetrahedra of four oxygen ions with a central ion of Si
1
,Al
1
,
P
1
, etc.
SBUs
Single rings: S-4, S-5, S-6, S-8, S-10, S-12
Double rings: D-4, D-6, D-8
Larger symmetrical
polyhedra
Truncated octahedron (T.O.) or sodalite unit
11-hedron or cancrinite unit
14-hedron or gmelinite unit
Si
4+
, Al
3+
, etc.
O
2-
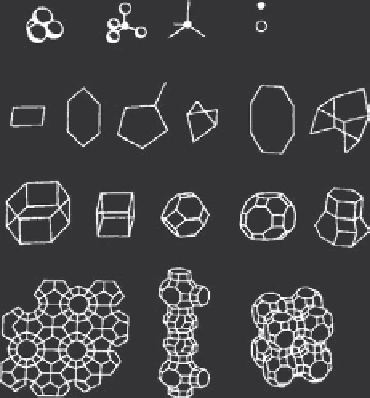
(a) Primary units
(b) Secondary units
(c) Tertiary units
or building
polyhedra
(d) Zeolite structures
Melanoplogite
Paulingite
Rho
Figure 6.4 Development of zeolite structures
[28]
.
structure of zeolites, the corners of the polyhedra represent Si or Al atoms and the
connecting lines represent the shared oxygen atoms. Individual structures may
comprise only one basic unit or many of them. A record is held by the mineral
paulingite, which contains five such polyhedra.
Different combinations of the same SBU may give numerous distinctive zeolite
structures.
Figure 6.5
shows an example of three different zeolites that have the same
structural polyhedron (cubo-octahedron), but probably form from smaller ring units.
The IUPAC commission on zeolite nomenclature has framed rules and designa-
tions consisting of three letters that have been used through the assignment of
structure-type codes
[29]
. This is subjected to review and clearance by the IZA