Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
1
9
2
3
4
10
6
7
11
5
8
600
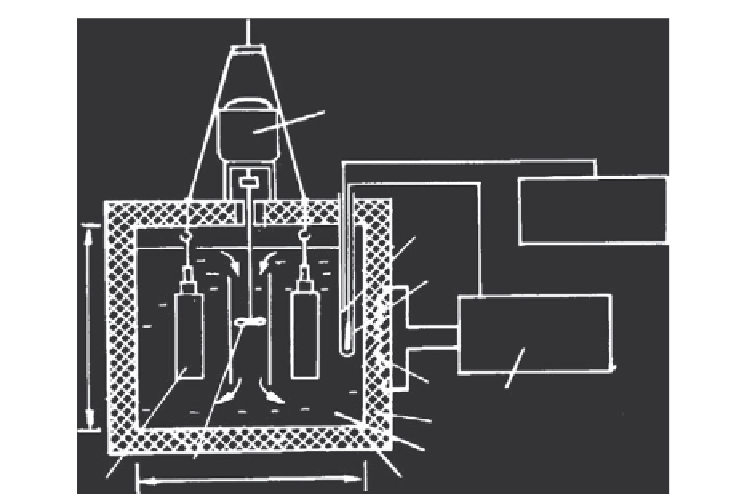
Figure 3.22 An assembly for studying solubility simultaneously in two autoclaves
[58]
.
(1) Motor, (2) thermocouple, (3) sensor, (4) heater, (5) autoclave, (6) body of furnace, (7)
salt solution, (8) thermal insulation, (9) potentiometer, (10) electronic regulator, and (11)
stirrer.
complete the separation of the crystals from the solution, and then it must be cooled
to room temperature by an electric fan or cooling fan. The crystals are separated
from the solution under the hydrothermal condition vapor phase during cooling.
The solubility calculated from the weight loss of the crystals must be accurate as
the crystals do not dissolve in water vapor, because this method totally hinders the
regrowth of crystals with a positive temperature coefficient of solubility, and redis-
solution of the crystals with a negative temperature coefficient. Using this autoclave,
the authors have accurately determined the solubility of berlinite in phosphoric acid
and calcinite in ammonium chloride solution and their results match well with the
earlier published data
[60
62]
.
Figure 3.24
a and b shows the solubility data for
berlinite.
Rocking Autoclaves
These are more versatile designs for carrying out a variety of hydrothermal
experiments including measurements of mineral and gas solubilities, mineral phase
stabilities, kinetics of mineral transformations, stable isotope fractionation factors,
experiments involving crystal growth, and the formation of synthetic fluid