Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
design, as the number exceeds 100. However, a majority of them are only to suit a
specific aspect of hydrothermal research and hence are not versatile. Therefore, for
the sake of simplicity, we have discussed only the more universal autoclave designs
under the two broad classes: (1) conventional autoclave designs and (2) novel auto-
clave designs.
3.5.1 Conventional Autoclave Designs
These are the more universal designs commercially available for general hydrother-
mal research. The designing of the conventional autoclaves began in mid-nineteenth
century, and simple glass vessels were the earliest members of this category. Let us
discuss some conventional autoclaves one by one.
Glass Vessels
The glass vessel in hydrothermal research has advantages of ease of observation
and resistance to acid solutions (except HF acid). The disadvantages are the low
pressure
temperature conditions and ease of attack by basic solutions. Hence, its
use has been generally neglected in hydrothermal work, mainly because the early
interest concerned materials requiring basic media and pressure
temperature con-
ditions beyond the limits of glass. When the solvent and pressure
temperature con-
ditions permit and the visual observation enables, glass vessels have much to their
recommendation and should be used more frequently in hydrothermal work. Before
the design of Morey-autoclaves in 1913, the hydrothermal vessels consisted of
tubes loaded with solid and water and sealed either by welding both the ends of the
tube or by means of a flat washer or screw. However, such vessels are very difficult
to maintain and dangerous to operate. Croxall et al. (1979) from General Electric
Company, UK, have successfully grown berlinite crystals using glass vessels
[27]
.
Sealed quartz glass tubes were first tried successfully as pressure vessels in 1964
by Speed and Filice
[6]
. Quartz autoclaves are good for low pressure
temperature
hydrothermal experiments in silica-saturated systems. These tubes provide an inex-
pensive means for making simultaneous runs along an isotherm with varying bulk
composition, pH, partial gas pressure, etc., within a single heater.
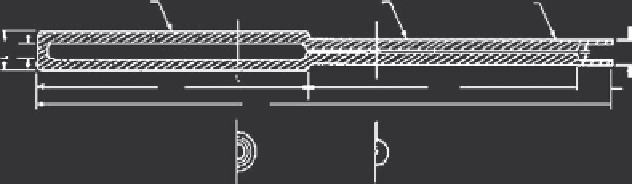
Figure 3.8
shows
Approx. seal-off
position
Quartz glass
capillary
Nested quartz
glass tubes
Charge chamber
1.27
91.5
88.8
12.7
93.1
Sections
Figure 3.8 The cross sections of quartz glass tube
[6]
.