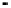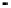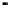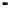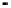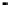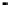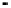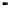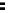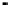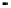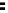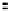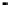Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
SRAM cache
memory
SRAM cache
memory
SRAM tag address
DRAM
addresses
Address
bus
System
Controller
DRAM
memory
System
Controller
DRAM
memory
Processor
Processor
DRAM
Data bus
Data
bus
PCI bus connections
(typically up to 5 devices)
Motherboard clock
speed
Local
SRAM
cache
Local
SRAM
cache
Bus
bridge
Bus
bridge
Processor clock
speed
Differing clock
speeds
ISA bus IDE bus USB bus
Figure 2.22
Local bus architecture
An example PC motherboard is illustrated in Figure 2.23. The main components are:
•
Processor
. The processor is typically a Pentium processor, which has a SEC (single-
edge connector) or fits into a socket. The processor can run at a faster rate than the rest
of the motherboard (called clock multiplication). Typically, the motherboard runs at
50MHz, and the clock rate is multiplied by a given factor, such as 500MHz (for a ·10
clock multiplier).
•
System controller
. Controls the interface between the processor, memory and the PCI
bus.
•
PCI/ISA/IDE Xcelerated Controller
. Controls the interface between the PCI bus and
the ISA, USB and IDE busses.
•
I/O controller
. Controls the interface between the ISA and the other busses, such as the
parallel bus, serial bus, floppy disk drive, keyboard, mouse, and infrared transmission.
•
DIMM sockets
. This connects to the main memory of the computer. Typically it uses
either EDO DRAM and SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM). SDRAM transfers data faster
than EDO DRAM as its uses the clock rate of the processor, rather than the clock rate of
the motherboard.
•
Flash memory
. Used to store the program which starts the computer up (the boot proc-
ess).
•
PCI connectors
. Used to connect to PCI-based interface adaptors, such as a network
card, sound card, and so on.
•
ISA connectors
. Used to connect to ISA-based interface adaptors, such as a sound
cards.
•
IDE connectors
. Used to connect to hard disks or CD-ROM drives. Up to two drives