Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
MN/
-
MX
CLK
READY
RESET
GND
8284
Clock
Generator
CLK
-
S
0
-
S
1
-
S
2
-
S
0
-
S
1
-
S
2
-
MEMR
-
MEMW
-
IOR
-
IOW
-
INTA
DEN
DT/
-
R
ALE
8088
Processor
8288 Bus
Controller
8088
Processor
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
40
V
CC
STB
A14
39
A15
Address
bus
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
NMI
INTR
CLK
GND
38
A16/S3
AD0-AD19
A16-A19
37
A17/S4
36
A18/S5
Latch
35
A19/S6
34
SSO
DIR
-
G
33
MN/
-
MX
32
-
RD
Data
bus
31
-
RQ/
-
GT0
INTR
30
-
RQ/
-
GT1
Buffer
29
-
LOCK
28
-
S2
27
-
S1
26
-
S0
IRQ0
IRQ1
IRQ2
25
QS0
8259
Interrupt
controller
24
QS1
Interrupt
requests
23
-
TEST
22
READY
20
21
RESET
IRQ7
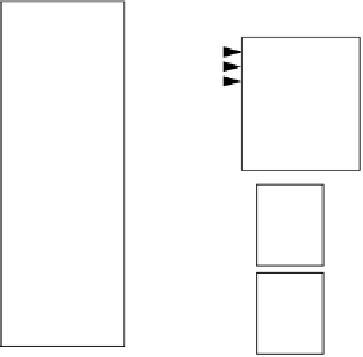
Figure A.1
8088 connections
Registers
Each of the PC-based Intel microprocessors is compatible with the original 8086 processor
and are normally backwardly compatible. Thus, for example, a Pentium can run 8086 and
80386 code. Microprocessors use registers to perform their operations. These registers are
basically special memory locations in that they are given names. The 8086/88 has 14 regis-
ters which are grouped into four categories, as illustrated in Figure A.2.
General-purpose registers
There are four general-purpose registers which are AX, BX, CX and DX. Each can be used
to manipulate a whole 16-bit word or with two separate 8-bit bytes. These bytes are called
the lower and upper order bytes. Each of these registers can be used as two 8-bit registers;
for example, AL represents an 8-bit register which is the lower half of AX and AH represents
the upper half of AX.
The AX register is the most general purpose of the four registers and is usually used for
all types of operations. Each of other registers have one or more implied extra functions:
•
AX is the accumulator. It is used for all input/output operations and some arithmetic op-
erations. For example, multiply, divide and translate instructions assume the use of AX.
•
BX is the base register. It can be used as an address register
•
CX is the count register. It is used by instructions which require to count. Typically is it
is used for controlling the number of times a loop is repeated and in bit shift operations.
•
DX is the data register. It is used for some input/output and also when multiplying and
dividing.