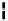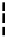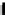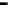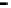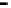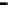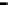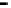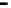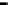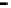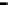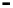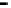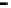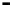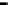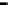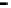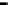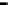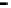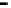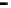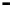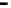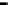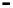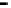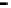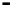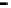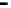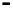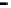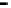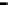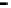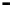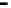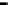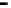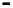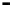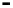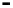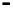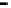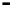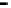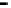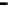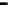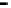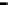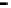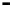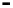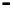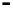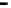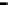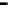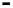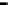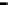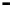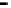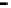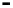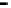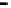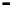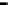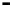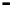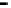Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Router
Network
Network
Data Link
Data Link
A router routes with
the network address
(such as the IP address)
Physical
Physical
Bridge
Data Link
Data Link
A bridge routes with
the MAC address
Physical
Physical
Repeater
A repeater boosts the
signal
Physical
Physical
Figure 25.9
Repeaters, bridges and routers
25.4.2 Bridges
Bridges filter input and output traffic so that only data frames distended for a network are
actually routed into that network and only data frames destined for the outside are allowed
out of the network.
The performance of a bridge is governed by two main factors:
•
The filtering rate
. A bridge reads the MAC address of the Ethernet/Token ring/FDDI
node and then decides if it should forward the frames into the network. Filter rates for
bridges range from around 5000-70 000 pps (packets per second).
•
The forward rate
. Once the bridge has decided to route the frame into the internetwork,
the bridge must forward the frame onto the destination network. Forwarding rates range
from 500 to 140 000 pps and a typical forwarding rate is 90 000 pps.
A typical Ethernet bridge has the following specifications:
Bit rate 10 Mbps
Filtering rate 17 500 pps
Forwarding rate
11 000 pps
Connectors
Two DB15 AUI (female), one DB9 male console port, two BNC
(for 10BASE2) or two RJ-45 (for 10BASE-T).
Algorithm
Spanning tree protocol. This automatically learns the addresses of all
devices on both interconnected networks and builds a separate table for
each network.