Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 23.4
Internet domain assignments for web servers
Web server
Internet domain name
Internet IP address
NEC
web.nec.com
143.101.112.6
Sony
www.sony.com
198.83.178.11
Intel
www.intel.com
134.134.214.1
IEEE
www.ieee.com
140.98.1.1
University of Bath
www.bath.ac.uk
136.38.32.1
University of Edinburgh
www.ed.ac.uk
129.218.128.43
IEE
www.iee.org.uk
193.130.181.10
University of Manchester
www.man.ac.uk
130.88.203.16
23.8 Internet naming structure
The Internet naming structure uses labels separated by periods; an example is
eece.napier.ac.uk
. It uses a hierarchical structure where organisations are grouped into
primary domain names. These are
com
(for commercial organisations),
edu
(for educational
organisations),
gov
(for government organisations),
mil
(for military organisations),
net
(Internet network support centers) or
org
(other organisations). The primary domain name
may also define the country in which the host is located, such as
uk
(United Kingdom),
fr
(France), and so on. All hosts on the Internet must be registered to one of these primary do-
main names.
The labels after the primary field describe the subnets within the network. For example in
the address
eece.napier.ac.uk
, the
ac
label relates to an academic institution within the
uk
,
napier
to the name of the institution and
eece
the subnet within that organisation. An exam-
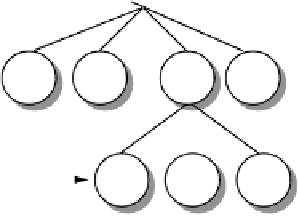
ple structure is illustrated in Figure 23.10.
edu
gov
com
mil
usa
uk
fr
ac
intel
sony
nec
ed
bath
napier
man
eece.napier.ac.uk
eece
cs
mmse
www.eece.napier.ac.uk
www
Figure 23.10
Example domain naming