Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
•
Eight data lines (DIO1…DIO8). These allow eight bits to be transmitted, at a time. If
more than eight bits are to be transmitted then they are sent one at a time. This gives a
maximum throughput of 1 M
B/s.
•
Three handshaking lines ( DAV , NRFD and NDAC ). These handshake the data be-
tween a talker and a listener.
•
Five bus management lines (IFC, ATN, SRQ, REN and EOI). These provide status in-
formation on the bus.
Talker/Listener
Talker/Listener
Talker/listener
Talker/listener
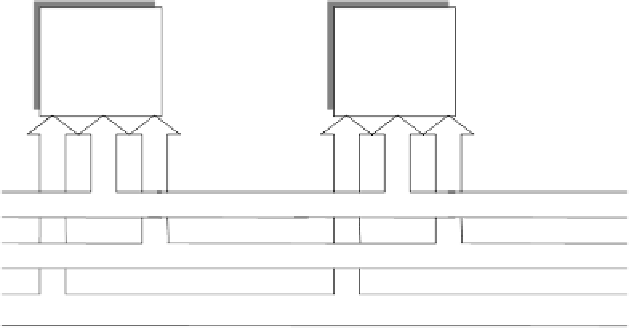
Data bus (DIO1-DIO8)
Management lines (ATN, IFC, SRQ, REN and EOI)
Handshaking lines (DAV, NRFD and NDAC)
Figure 22.1
IEEE-488 bus lines
The IEEE-488 bus is a bidirectional bus where data can flow in either direction. Devices are
set up with their functionality. These are either a talker, a listener or a controller, or any com-
bination of these. The function types are:
•
Talkers -
t
hese are devices which can send data to other devices or to the control. These
include multi-meters and oscilloscopes. Only one device is allowed to talk at a time.
•
Listeners - these are devices which only receive data. A device can also be a talker and a
listener. For example, a multimeter can be a talker when it is sending voltage samples,
but a listener when it is receiving data on range changes.
•
Controller - these are devices which are responsible for information management on the
bus, and include setting up tasks, monitoring the progress of measurements and interpret-
ing results. To avoid a conflict, only one controller may be active at any time, but there
may be more than one controller connected to the bus. Thus a controller can pass control
to another controller.
It is possible to construct a system which does not have a controller and only has a talker and
a listener. For example, a talker could be a digital multimeter and the listener could be a
printer. The multimeter is then hardwired as a talker (using switches) and the printer as a
listener.
22.2.1 Signal lines
Figure 22.2 shows the connections on the GPIB connector. Each instrument on the bus has
an assignable and unique address on the bus. These addresses are selected by switches, al-