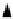Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
0
b
0
b
1
b
2
b
3
b
4
b
5
b
6
P
S1
S2
1
start
bit
Parity
bit
Stop
bit(s)
ASCII
character
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
'A' (100 0001)
Figure 13.5
RS-232 frame format
Example
An RS-232 serial data link uses 1 start bit, 7 data bits, 1 parity bit, 2 stop bits, ASCII coding
and even parity. Determine the message sent from the following bit stream.
First bit sent
⇓
11111010000010110000011111111111111000001111111100011001111010
10 0111111111111
Answer
The format of the data string sent is given next:
{idle}
11111
{start bit}
0
{'A'}
1000001
{parity bit}
0
{stop bits }
11
{start bit}
0
{'p'}
0000111
{parity bit}
1
{stop bits}
11
{idle}
11111111
{start bit}
0
{'p'}
0000111
{parity bit}
1
{stop bits}
11
{idle}
11
{start bit}
0
{'L'}
0011001
{parity
bit}
1
{stop bits}
11
The message sent was thus 'AppL'.
Parity
Error control is data added to transmitted data in order to detect or correct an error in trans-
mission. RS-232 uses a simple technique known as parity to provide a degree of error detec-
tion.
A parity bit is added to transmitted data to make the number of 1s sent either even (even
parity) or odd (odd parity). It is a simple method of error coding and only requires exclusive-
OR (XOR) gates to generate the parity bit. The parity bit is added to the transmitted data by