Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
tl
(6 bits)
rtl
(2 bits)
tcode
(4 bits)
prl
(4 bits)
Destination ID (16 bits)
Source ID (16 bits)
Destination offset (48 bits)
Data length (16 bits)
Extended tcode (16 bits)
Header CRC (32 bits)
Data field
Zero padded bytes (8n bits)
Data CRC (32 bits)
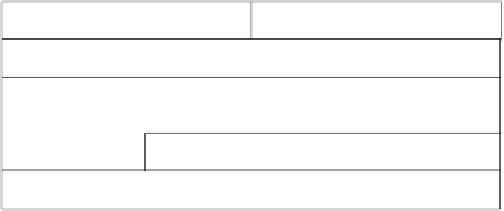
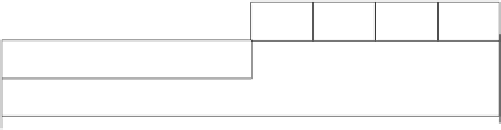
Figure 9.3
Asynchronous write data block payload
9.3.3 IEEE-1394 packet formats
There are a number of different packet formats specified in 1394-1995, however only the
asynchronous block write will be presented here, as it is the main transaction type used
within this project.
The asynchronous block write is described in the 1394-1995 specification as a packet
type that requests a data block be written to the specified destination address. It is the packet
type used on asynchronous transmits, for a variable length of data.
The destination_ID field should contain the 16-bit destination node ID, while the destina-
tion_offset field contains the remaining 48 bits required for CSR addressing. The data is sent
in the data field, which can be any quadlet-aligned length up to a maximum given by the
transmission speed. At 200 Mbps, for example, the data field may hold anything from 0 to
1024 bytes, in stages of four bytes. The header information is followed by a CRC (cyclic
redundancy check) for error checking, as is the block of data.
9.3.4 Bus management
Two bus management entities are available in the cable environment: the isochronous re-
source manager and the bus manager. They provide services such as maintaining topology
maps, or acting as a central resource from which bandwidth and channel allocations can be
made. Further information on bus management can be found in the 1394-1995 specification.
9.3.5 Cable
Figure 9.4 shows that the 1394 cable consists of three individually shielded cable pairs.
There are two power lines and two (screened) twisted pairs for data and strobe transmission.
9.3.6 Transmission rates
As already discussed, the cable rate definitions for 1394-1995 are termed S100, S200 and
S400, give actually data rates of 98.304 Mbps, 196.608 Mbps and 393.216 Mbps, respec-
tively. The high data rates are achieved by using differential non-return to zero (nrz), signal-
ling on each shielded twisted pair.