Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Sector 1
(512 bytes)
Track 0
Track 40
Sector 2
(512 bytes)
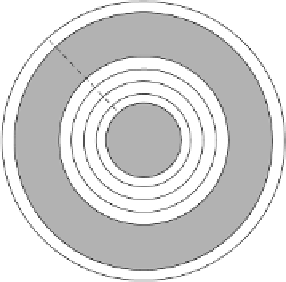
Figure 6.1
Tracks and sectors on a disk
Figure 6.1 also shows how each track is split into a number of sectors, in this case there are
eight sectors per track. Typically each sector stores 512 bytes. The total disk space, in bytes,
will thus be given by
Disk space = Number of sides
×
tracks
×
sectors per track
×
bytes per sector
For example, a typical floppy disk has two sides, 80 tracks per side, 18 sectors per track and
512 bytes per sector, so
Disk capacity
= 2
×
80
×
18
×
512
= 1 474 560 B
= 1 474 560/1 024 KB
= 1 440 KB
= 1440/1024 MB
= 1.4 MB
6.3 Floppy disks
A 3.5-inch DD (double density) disk can be formatted with two sides, nine sectors per track
and 40 tracks per side. This gives a total capacity of 720 KB. A 3.5 inch HD (high density)
disk has a maximum capacity when formatted with 80 tracks per side.
A 5.25-inch DD disk can be formatted with two sides, nine sectors per disk with either 40
or 80 tracks per side. The maximum capacity of these formats is 360 KB (40 tracks) or 720
KB (80 tracks). A 5.25-inch HD disk can be formatted with 15 sectors per track which gives
a total capacity of 1.2 MB. When reading data the disks rotate at 300 rpm. Table 6.1 outlines
the differing formats.
Table 6.1
Capacity of different disk types
Size
Tracks per side
Sectors per track
Capacity
5.25 -inch
40
9
360 KB
5.25-inch
80
15
1.2 MB
3.5-inch
40
9
720 KB
3.5-inch
80
18
1.44 MB