Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.1 Supratidal Marshes and Mangroves
Along modern temperate shorelines, the supratidal area may be vegetated by
salt marshes, the cordgrass
Spartina
being one of the most widespread plants,
their root traces being typically pervasive in such deposits (
Fig. 2
; e.g.,
Basan
and Frey, 1977; Edwards and Frey, 1977; Montague et al., 1981; Pomeroy et al.,
1981
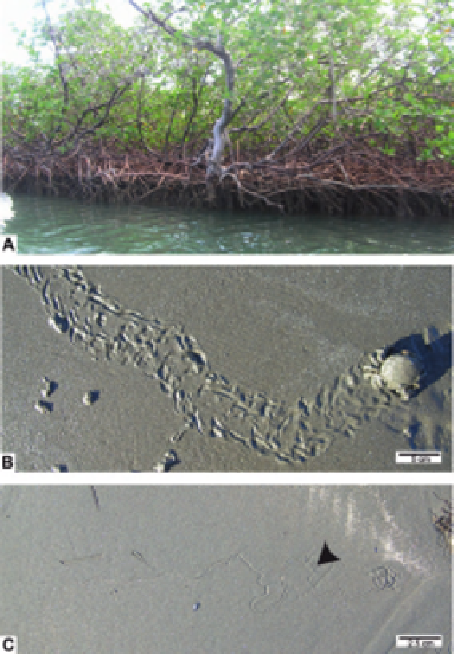
). Along tropical shorelines, mangroves tend to be common, allowing the
formation of extensive root networks of, for example,
Avicennia
,
Rhizopora
,
and
Sonneratia
(
Fig. 3
A;
Cad
´
e, 1998
). Animal traces include elements of
the
Psilonichnus
Ichnofacies, with gastropods and crustaceans (mainly crabs)
forming some of the most important marine elements (
Frey and Pemberton,
1987
;
Fig. 2
). The beetle
Bledius arenarius
typically constructs dwelling bur-
rows (
Sch¨fer, 1972
). Insects are by far
the most
important
terrestrial
FIGURE 3
Modern mangrove and mud flats. (A) Modern mangrove. Gran Mangle, Dominican
Republic. (B) Crab trackway on a modern mud flat near Estancia Maria Luisa, Tierra del Fuego,
southern Argentina. (C) Grazing trail on a modern mud flat between Cabo Irigoyen and Cabo
San Pablo, Tierra del Fuego, southern Argentina.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search