Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Paleokarst, caliche,
salinas and hypersaline
ponds or lagoons
Evaporitic platform with
tidal flats, ponds,
sand deposits,
channels, and sabkha
Below storm
wave base
Lagoon with restricted
circulation, tidal flats
and ponds
Normal marine lagoon
with sand waves and
washover deposits
Elongated shoals, tidal
bars and beaches,
eolianites
Storm-reworked
sand shoals
Sand waves with
reworked platform
material and
interbedded mud
Legend
Platform interior
Sea
Mud-dominated
carbonates
Sand-dominated
carbonates
Sabkha and salina
Tidal flat
Restricted lagoon
Open lagoon
Platform margin
Shoreface/
inner ramp
Slope/
outer ramp
Basin/
deeper intra-shelf
Normal wave base
Pedogenic carbonates
overprinting supratidal
and intertidal deposits
Laminated dolomitic
mudstone, bindstone,
grainstone, packstone,
gypsum, and anhydrite
Storm wave base
Dolomitic mudstone
and wackestone,
subordinate grainstone
Mudstone and wacke-
stone with packstone
and grainstone interbeds
Clean grainstone and
packstone
Packstone and
grainstone
Grainstone, wackestone,
and mudstone
Fossiliferous mudstone
and marlstone, inter-
bedded with wacke-
stone and grainstone
Cylindrichnus
Skolithos
Balanoglossites
Macaronichnus
Asterosoma
Zoophycos
Arenicolites
Planolites
Taenidium
Plant roots
Bl
Ichnodiversity
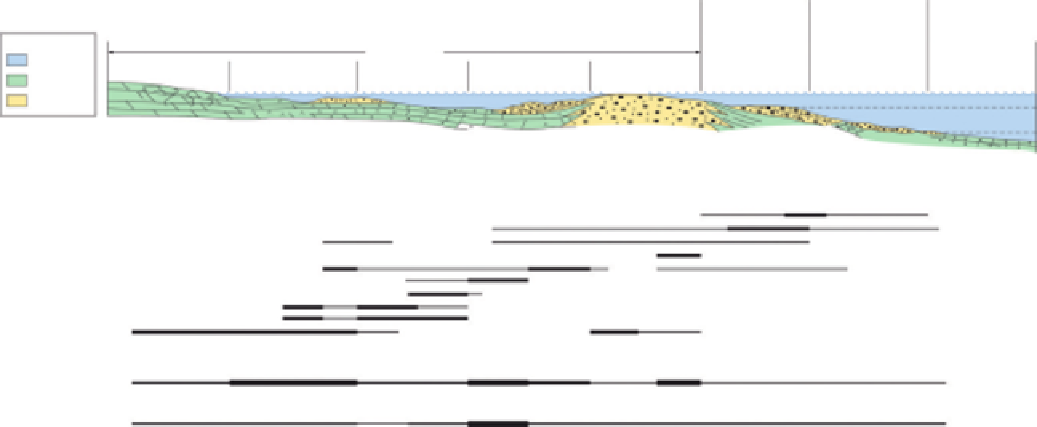
FIGURE 12
Generalized cross section of the Khuff carbonate platform in the Persian Gulf area from south (proximal to the left) to north (distal to the right), based on
Wilson (1975)
. The simplified facies zones are based on sedimentological and ichnological core observations and are the building blocks of small-scale shallowing-
upward sequences. The bars in the lower part refer to recognized trace-fossil assemblages, bioturbation index (BI), and ichnodiversity with increasing abundance
(rare, moderate, and abundant).
From
Knaust (2009)
.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search