Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Puree/pulp derivates
A number of products may be produced from guava
puree/pulp such as juices, toppings, ice creams, jams, and
jellies. The selection of guavas for these products is limited
to the removal of rotten and damaged fruits because the dif-
ferences in size and flesh firmness are irrelevant since the
material will be homogenized and standardized according
to the soluble solids/sugar content. Generally, fully ripened
fruits with firm consistency and attractive color (for red
varieties), high acidity and ascorbic acid content, but with
few seeds are preferred for puree processing (Martin and
Kato, 1988). However, the part of the seeds and flesh that
are removed from the fruits for the processing of osmoti-
cally dehydrated or canned guava may also be used in puree
processing.
The fruits must be properly washed and sanitized before
being chopped or sliced. The chopped guava may either
be mashed or grinded in a pulper. The pulper removes the
seeds and fibrous material from the tissue besides forcing
the remainder of the product through a perforated screen.
However, in the absence of a pulper, a sieving step may
also be used for this purpose. After the pulper, the puree
may either be passed through a finisher or through a mill to
remove or grind the stone cells, respectively. Care should
be taken in this latter technique since the incorporation of
a large amount of stone cells into the puree may discolor
it (Yusof, 2003). Another method for puree extraction con-
sists of cooking the fruit before pulping it, which may lead
to degradation of the vitamin C and other labile compounds,
reducing the quality of the final product (Martin and Kato,
1988). After production, the guava puree may be preserved
by freezing (frozen guava puree), chemical preservatives,
canning (canned guava puree), or by using aseptic pack-
aging prior to being destined for other processes (Martin
and Kato, 1988; Adsule and Kadam, 1995; Dauthy, 1995)
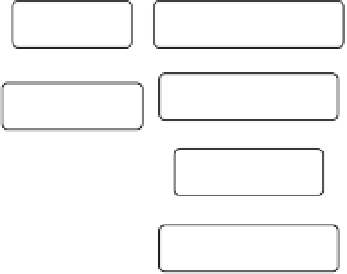
(Fig. 11.4).
Some characteristics of the fresh guava puree obtained
from both white and pink fruits are given in Table 11.2.
Raw guava
Sorting
Washing/Sanitizing
Cutting/Slicing
Cooking
Pulper
Finisher
Preservative
addition
Pasteuri
zation
Sterili
zation
Packing
Hot filling
Cooling
Freezing
Packing
Cooling
Packing
Storage at room
temperature
Storage
Storage
Figure 11.4.
Flow diagram of guava puree processing.




Search WWH ::

Custom Search