Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
1.10 Type II Fuzzy Set
Membership functions are usually defined by the expert and are based
on his or her intuition or knowledge. So, different fuzzy techniques differ
mainly in the way that they define the membership function, and so dif-
ferent results are obtained using different types of membership functions.
To find a more robust solution, Type II fuzzy sets are introduced. There are
different sources of uncertainties in type I fuzzy sets; they are (1) inaccurate
measurements, (2) disagreement of the membership values with the accurate
membership values of the data that are used to tune Type II fuzzy set and (3)
uncertainty in the location, shape or other parameters. According to Mendel
and John [12], 'Type I fuzzy sets are not able to directly model such uncer-
tainties because their membership functions are totally crisp. On the other
hand, Type II fuzzy sets are able to model such uncertainties because their
membership functions are themselves fuzzy'. If there is no uncertainty, then
a Type II fuzzy set reduces to a type I fuzzy set. Type II fuzzy set is obtained
by blurring the type I fuzzy set. So, Type II fuzzy sets are the fuzzy sets for
which the membership function is not a single value for every element but
an interval. A Type II fuzzy set may be written as
μ
A
Type II
=
{, ()|}
x xxX
A
∈
where
A
µ
is the Type II membership function. The footprint of uncertainty
(FOU) represents the uncertainty in the primary memberships of the Type II
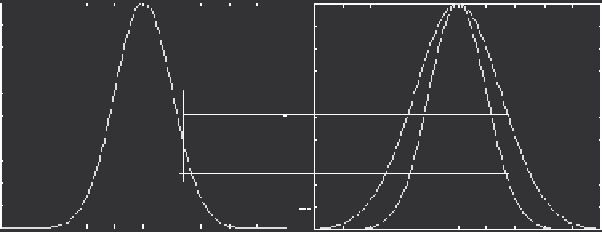
fuzzy set as shown in Figure 1.1 [9].
()
Ty pe I fuzzy set
Ty pe II fuzzy set
1
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
Upper level
Membership
Lower level
0
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 1.1
(a) Type I membership function and (b) interval of Type II fuzzy membership function in
the FOU.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search