Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
The
IFD
between
A
and
B
,
IFD
(
A
,
B
), is computed between each of the ele-
ments
a
ij
and
b
ij
of image window
A
and that of template
B
. It is given as
(
)
μ
() ()
a
−
μ
b
μ
() ()
b
−
μ
a
IFDa b
(,)
=−−
21
[ () ( ]
μ
a be
+
μ
⋅
Aij Bij
−−
[
1
μ
(() ( ]
b
+
μ
a
⋅
e
Bij Aij
ij
ij
Aij
B
ij
B
ij Aij
(
μ
() ()(()
a
−
μ
b
−
π
b
−
π
(
a
))
+−−
21
[(()(())
μ
a
−
μ
b
+
((()
π
b
−
π
(
a
))]
⋅
e
Aij Bij Bij Aij
Aij
B
ij
Bij
A
ij
)
π
() ()(
b
−
π
a
−
μ
() ( )
a
−
μ
b
−
[
1
−
(()
π
b
−
π
(
a
)) (()
+
μ
a
−
μ
(
b
))]
⋅
e
Bij Aij
AAij Bij
Bij
A
ij
Aij
B
ij
(8.2)
Normalized values of the (
i
,
j
)th pixel of image
A
are the membership
degrees, μ
A
a
ij
, while the values of the template are the membership degrees
of the template pixels, μ
B
b
ij
:
π
(,)
ab c
=∗−
(
1
μ
(,))
a b
Aij
ij
A
ij
ij
where
c
is a hesitation degree. The value of
c
should be such that π
A
(
a
ij
) +
μ
A
(
a
ij
) + ν
A
(
a
ij
) = 1 holds.
IFD
(
a
ij
,
b
ij
) is the
IFD
between each element of the template (
b
ij
) and the
image window (
a
ij
). It is calculated for all pixel positions of the image. Finally,
an
IFD
matrix, which is of the same size as that of the image, is formed. This
IFD
matrix is thresholded and thinned to get an edge-detected image. Then
the threshold is selected manually for getting the final edge-detected result.
Example 8.1
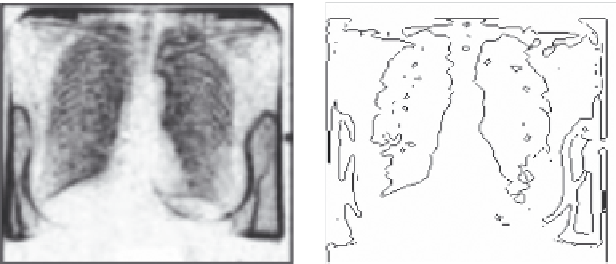
An example in Figures 8.1 and 8.2 will illustrate the effectiveness of intu-
itionistic fuzzy edge detection directly on medical images. Figure 8.1 is a
lung image and Figure 8.2 is a brain image.
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 8.1
(a) Lung image and (b) edge-detected image. (Modified from Chaira, T. and Ray, A.K.,
Appl.
Soft Comput.
, 8(2), 919, 2007.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search