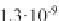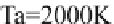Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Branch coefficients for the chemo-ionization in Na
*
(
n
eff
,
l
Fig. 1.17
D
1)
C
Na collisions;
cb
and
c
denote the crossed beams and vapor cell, respectively.
T
D
800-900 ›
Tabl e 1. 7
Rate constants of
AI reaction with the
formation of homogeneous
and heterogeneous molecular
ions,
T
D 450 K
k
AI
10
10
k
AI
10
10
cm
3
s
1
cm
3
s
1
Ion KRb
C
Ion Rb
2
State
6
2
D2.4
˙
0.6
1.6
˙
0.4
8
2
S
2.4 ˙ 0.6
2.2 ˙ 0.7
7
2
D2.5
˙
1.0
2.3
˙
0.9
Klyucharev and Lazarenko (
1980
). As a result, it is possible to estimate the constant
value lower limit
k
min
> 10
10
cm
3
s
1
for the asymmetrical chemo-ionization
processes. Thus, the values of the constants of the asymmetrical processes involving
Rydberg atoms in the thermal range of speeds can reach significant values. The
process of the ion HeNe
C
(Ne
*
C
He) was studied by Harth et al. (
1986
). In this
case the measured value of the cross-section maximum at
n
eff
10 was an order of
magnitude smaller than those for the symmetrical Ne
*
C
Ne case.
A two-step excitation scheme via intermediate metastable states is used in this
work and in most of the others on studies of the inert gas Rydberg atoms. To do
this, the direct optical methods using a synchrotron and a laser (photon) excitation
have been actively used in recent years (Hu et al.
2000
). Estimates show that the
ratio of the effective rate constants of the reaction Na
*
(
n
2
P)
C
Na (Li) for the
principal quantum numbers 8
n
14 with the formation of homogeneous and
heterogeneous molecular ions should be smaller than unity. The experimental rate
constants of the AI reaction Rb(
n
,
l
)
C
K(4S)
!
KRb
C
C
e
are given by Djerad
et al. (
1985
). In Table
1.7
are presented the rate constant values for the 6
2
D, 8
2
S,
and 7
2
D states, and a comparison with the reaction Rb(
n
,
l
)
C
Rb(5
2
S).