Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
450
N
2
2
+
0-0
1-1
2-2
z=2.5 cm
Y=D mm
Y=7 mm
400
N
2
2
+
0-1
350
N
2
2
+
1-2
300
OHA-X
OHA-X
250
200
330
340
350
360
370
380
λ
, nm
Fig. 6.5
Typical optical spectra of longitudinal plasmoid created by capacity-coupled high-
frequency discharge in swirl flow. Distance
X
D
2.5 cm from the high frequency electrode for
two different distances from the tube axis
Y
D
0mmand
Y
D
7 mm;
V
t
30 m/s;
P
HF
D
240 W
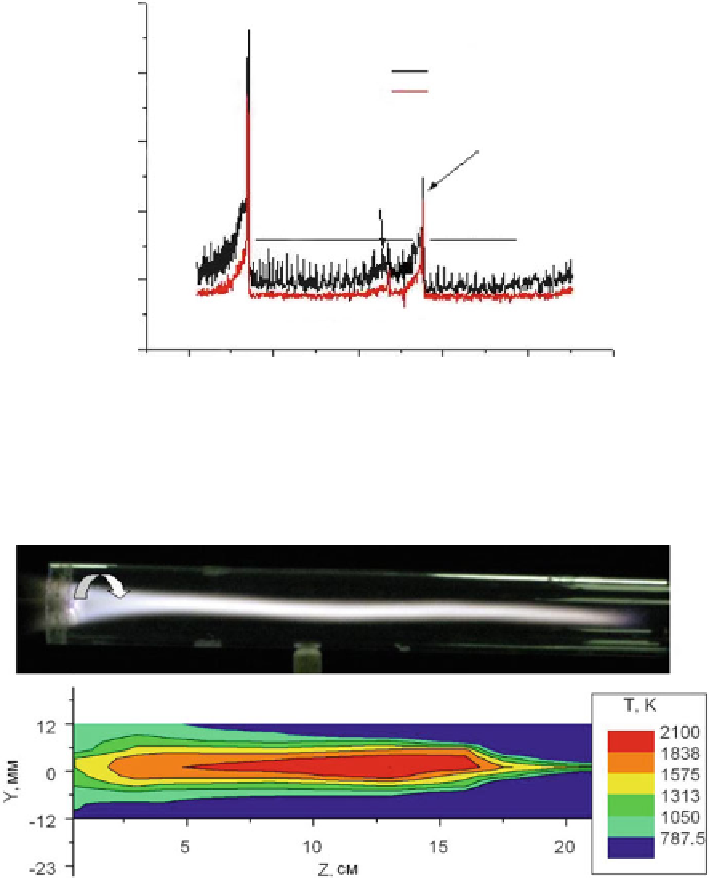
Fig. 6.6
Gas temperature (
K
) distribution in the high-frequency plasmoid, created in swirl flow.
V
t
D
30 m/s; high-frequency power
P
HF
D
240 W; pulse duration
T
i
D
1 ms; modulation frequency
10
5
F
M
D
500 Hz,
P
st
D
Pa.
To p
: Longitudinal high-frequency plasmoid in the swirl airflow
of the excited nitrogen molecules in this longitudinal vortex plasmoid. We have to
note that we could not create the longitudinal vortex plasmoid in a noble gas (for
example, argon), so it is most probably connected with the molecular features of
the gas.