Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
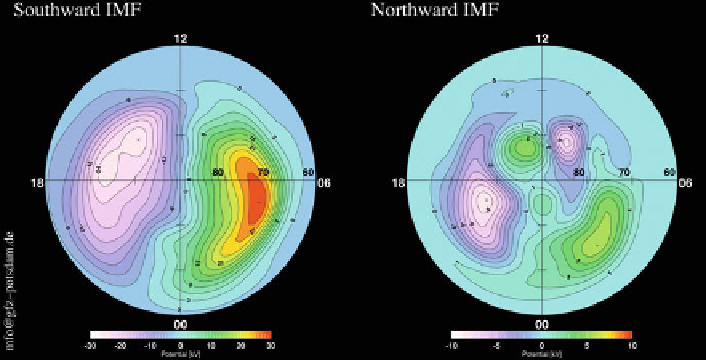
Fig. 4.1
Electric potential patterns for the Northern Hemisphere, as a function of the inter-
planetary magnetic field (IMF) orientation, derived from measurements of the Electron Drift
Instrument (EDI) on board the Cluster S/C (F orster et al.
2007
; Haaland et al.
2007
). Patterns
represent statistical averages of the large-scale magnetospheric circulation, mapped into the polar
ionosphere, for (
a
) southward and (
b
) northward IMF conditions. Note the different color scale
ranges: three times larger for the
left panel
Figure
4.1
illustrates the results obtained by this kind of studies, showing the high
variability of the plasma drift pattern in dependence on the IMF orientation. The left
panel is a statistical average of strict southward IMF (large negative IMF
B
z
values
in Geocentric Solar Magnetospheric (GSM) coordinates), where the energy and
momentum transfer from the solar wind by front-side reconnection is most effective,
and the right panel shows a four-cell pattern that develops under strict northward
IMF conditions (positive IMF
B
z
). The contrast between these two patterns of
different IMF orientation illustrates the 'bandwidth' of possible forcings.
On the other hand, the motion of the thermospheric neutral air across geomag-
netic field lines within the so-called ionospheric dynamo region (
80 to
175 km)
or in the F-layer dynamo region leads to the generation of internal electric fields.
The inertia of the thermospheric neutral winds can therefore help to maintain
the ionospheric-magnetospheric convection independently of the magnetospheric
driver processes; this has been known for long time as the flywheel effect (Banks
1972
; Coroniti and Kennel
1973
). The contribution of this thermosphere-ionosphere
interaction was already implied in Fig.
4.1
as part of the statistical average patterns.
4.3.2
The Climatological View: Statistically Averaged Patterns
The CHAllenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP) mission was launched in July
2000 into a circular near-polar orbit with 87.3
ı
inclination, initially at an altitude of