Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Zn
NEIL1
MvNei1
Fpg lesion
recognition loop
Zinc/
zincless
finger
C-terminal
domain
N-terminal
domain
F
IG
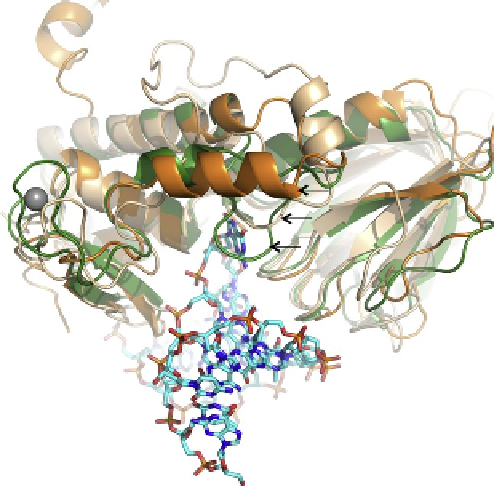
. 3. Superposition of BstFpg (E3Q mutant, green) bound to DNA containing 8-oxoG with
human NEIL1 (orange) and MvNei1 (beige). Overall, the three proteins superimpose well with an
RMSD of 1.1-1.3
˚
upon aligning C-
of analogous residues from the NEIL1 and MvNei1 with
BstFpg (performed using COOT
93
and Superimpose; M. Rould, personal communication). Key
differences among the three enzymes are the zinc/zincless finger in Fpg versus NEIL1 and
MvNei1, and the presence of the lesion-recognition loop in Fpg. The 8-oxoG containing DNA is
displayed as a ball and stick model. (PDB ID codes for the BstFpg protein, NEIL1, and MvNei1 are
1R2Y, 1TDH, and 3A42, respectively).
a
The structure of human NEIL1 reveals the presence of a structural motif
composed of two antiparallel
-strands that mimic the zinc finger fold. This
motif superimposes well with the zinc finger of EcoNei and the bacterial Fpg
proteins
59,61
(
Fig. 3
). However, the canonical Cys residues and the loops
connecting the
b
-strands of the zinc finger are missing in NEIL1, which pre-
vents the coordination of a zinc atom (
Fig. 3
). This motif, termed ''zincless
finger,'' contains a highly conserved Arg277 residue, which, when mutated,
significantly diminishes glycosylase activity.
56,61
This zincless motif is also
harbored by MvNei1,
61,67
and the plant and fungal Fpg glycosylases (St ´phanie
Duclos, Pierre Aller, Pawel Jaruga, Miral Didzaroglu, Susan S. Wallace and
Sylvie Doubli ´ , Manuscript submitted to DNA Repair).
In summary, members of the Fpg/Nei family are structurally similar, but
display significant variations in conserved domains/motifs involved in DNA
interactions. One of the main differences between EcoNei and the bacterial
b