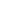Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
binding, thereby allowing the extruded base to be positioned in the active site
for catalysis. The minor groove is widened considerably at the lesion site;
however, the rest of the DNA duplex surrounding the lesion retains canonical
B-form.
55,59
Upon nucleotide eversion, three highly conserved residues in the
bacterial Fpg proteins, namely Met74, Arg109, and Phe111 (in EcoFpg), fill
the void that is created and stabilize the opposite base (
Fig. 2
A).
55
Met74 is part
of the
4/5 loop and occupies the position of the extruded base by entering
through the minor groove while Arg109 and Phe111 are part of a loop
b
A
B
A
(1)
G
(
-
1)
dRB1
Met74
P
(0)
Asn169
Arg259
(1)
A
P
(
-
1)
Phe111
G
(
-
1)
Arg109
Pro2
C
(1)
T
(
-
1)
Lys57
C
(0)
C
3
¢
5
¢
P
(
-
5)
P
(
-
4)
P
(
-
3)
P
(
-
2)
P
(
-
1)
P
(0)
P
(1)
P
(2)
P
(3)
P
(4)
G
*
G
(
-
4)
A
(
-
3)
A
(
-
2)
G
(
-
1)
A
(1)
G
(2)
G
(3)
A
(4)
C
(4)
T
(3)
T
(2)
C
(1)
C
(0)
T
(
-
1)
C
(
-
2)
C
(
-
3)
T
(
-
4)
P
(4)
P
(3)
P
(2)
P
(1)
P
(0)
P
(
-
1)
P
(
-
2)
P
(
-
3)
P
(
-
4)
P
(
-
5)
5
¢
3
¢
F
IG
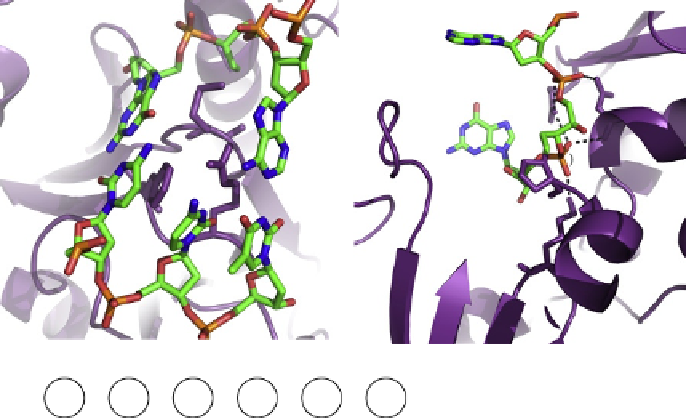
. 2. Specific interactions between EcoFpg and DNA. (A) Triad of void-filling residues
Met74, Phe111, and Arg109 that intercalate into the DNA, causing severe kinking at the site of the
damage. (B) Interaction of conserved residues Lys57, Asn169, and Arg259 with DNA phosphates
surrounding the ring-opened deoxyribitol moiety (dRb1) (PDB ID code 1K82
55
). (C) DNA
sequence context present in the crystal structure of EcoFpg bound to DNA, indicating the typical
nomenclature used to describe the phosphates and the bases surrounding the lesion. The lesion is
indicated by G* while C
(0)
is the opposite base, both of which are indicated in red lettering.