Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
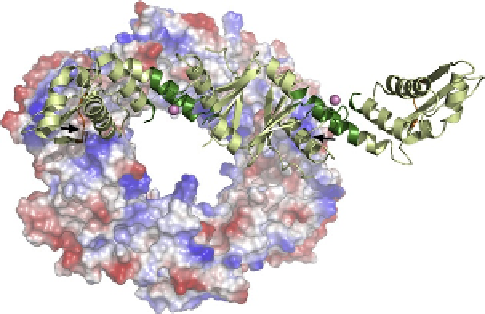
IG
. 8. Docking of MutL onto the structure of
b
. The structure of
B. subtilis
MutL-CTD
(PDB ID: 3KDK) is shown as a ribbon diagram superimposed onto the structure of
Streptococcus
pyogenes b
(PDB ID: 2AVT), depicted as an electrostatic potential surface. The endonuclease and
the
b
-binding motifs of BsMutL-CTD are colored dark green and orange, respectively, and the
regulatory zinc metal ion is depicted as a pink sphere. The two protein-binding grooves on the
surface of the sliding clamp are indicated with black arrows. (For interpretation of the references to
color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the online version of this chapter.)
Interestingly, the conserved QXXL[L/I]XP motif is also found in
E. coli
MutL and other MutL proteins that do not have endonuclease activity. How-
ever, disruption of this motif in
E. coli
MutL causes only moderate DNA
mismatch repair defects.
145
This is not surprising because it has been previ-
ously shown that
b
is dispensable for the MutH activation and strand excision
steps, despite being essential for overall mismatch repair in
E.
coli.
49
There-
fore, it has been proposed that the interaction between the C-terminal domain
of MutL and processivity clamp is only critical in organisms that lack the MutH
endonuclease.
96
Collectively, these findings strengthen the idea that in the
absence of MutH, PCNA and
b
likely coordinate the transfer of information
between the early steps in mismatch repair.
47,72,74,76,150
C. Mismatch Dependency
While we are starting to understand how the conformational changes
induced by ATP binding and the interaction with the processivity clamp
stimulate the endonuclease activity of MutL, the molecular mechanisms en-
suring mismatch dependency remain obscure. The interaction between MutS
a
and PCNA, or MutS and
b
in bacteria, increases the mismatch-binding spec-
ificity of MutS and recruits this mismatch-binding protein to sites of damage
and replication foci.
150-152
However, the interaction between PCNA and
MutS
a
is not required to activate mismatch excision, and mutation of the
PCNA-binding site confers only a modest increase in mutation rates.
139,153