Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
IG
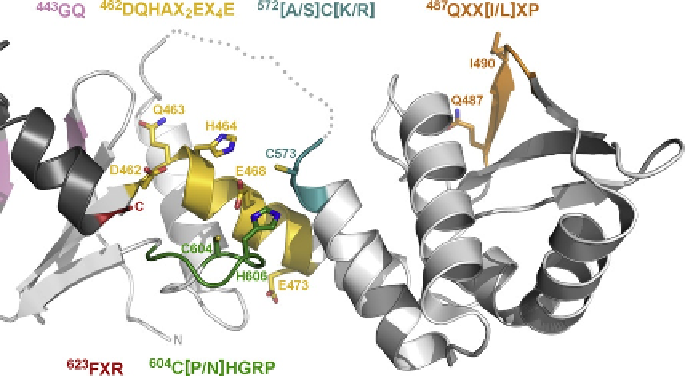
. 6. Organization of the endonuclease site of
B. subtilis
MutL. Ribbon diagram of the C-
terminal domain of
B. subtilis
MutL-CTD (PDB ID: 3KDK) shown in light gray with the C-
terminal helix of the neighboring protomer of the dimer shown in dark gray. The conserved motifs
related to the endonuclease activity of the protein are shown in pink (
443
GQ), yellow (
462
DQHAX
2-
EX
4
E), cyan (
572
SCK), green (
604
CPHRGP), and red (
623
FXR), with the strictly conserved residues
shown as color-coded sticks. The disordered loop connecting the external and dimerization domains
is shown as a dotted line. The N- and C-terminal ends of the domain are labeled
. The
conserved motif responsible for the interaction with the
b
-sliding clamp (
487
QXXIXP) is shown in
orange with the key residues shown as color-coded sticks and labeled.
N
and
C
conserved [A/S]C[K/R] motif at the linker connecting the
a
A and
a
E helices;
however, it is unlikely that it will adopt a similar conformation to that seen in
the structures of
B. subtilis
and
N. gonorrhoeae
MutL. Therefore, the [A/S]C
[K/R] motif presumably affects the endonuclease activity of MutL only mar-
ginally. The role of the conserved GQ motif is also unclear. In contrast to the
[A/S]C[K/R], C[P/N]HGRP, and FXR motifs that cluster around the endonu-
clease motif (DQHAX
2
EX
4
E), the GQ motif resides at the dimerization
interface (
Figs. 4 and 6
). However, it is close to the
a
D-
a
E loop and hence
may indirectly contribute to the overall stability of the endonuclease site.
Not all the conserved residues in the endonuclease motif are equally
important either (
Fig. 6
). For instance, mutation of the Gln463 or Glu473
(D
Q
HAX
2
EX
4
E
) does not disrupt mismatch repair activity in
B.
subtilis.
96
Similarly, mutation of the equivalent glutamic acid in hPMS2 (Glu710,
DQHAX
2
EX
4
E
) does not affect mismatch repair activity.
99
Conversely, muta-
tion of Asp462, His464, or Glu468 in
B. subtilis
MutL (
D
Q
H
AX
2
E
X
4
E) or the
corresponding residues in hPMS2 (Asp699, His701, and Glu705) completely
abrogates mismatch repair function.
67,96,99