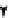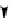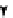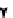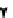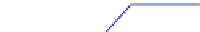Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Nick on template
Lesion on leading strand
Lesion on lagging strand
Ligation of leading strand
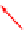
Fork regression by
branch migration
D-loop formation
D-loop formation
HJ resolution
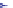
Synthesis of leading strand
HJ resolution &
replication fork restart
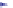
Replication fork restart
Branch migration &
replication fork restart
F
IG
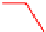
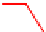
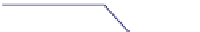
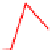
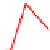
. 4. Homologous recombination (HR) restores collapsed or stalled replication forks. Nicks
of template strands lead to replication fork collapse, which can be repaired by D-loop formation and
Holliday junction cleavage to restore replication. A lesion on a leading strand may result in
replication fork regression and DNA synthesis on the leading strand. Subsequent branch migration
restores the replication fork.
where the blocked strand may invade the nascent complementary strand to
bypass the lesion by DNA synthesis (
Fig. 4
, right). Resolution of the resulting
Holliday junction may then restore replication.
B. DSB Recognition and End Resection
The substrate for HR is an ssDNA region with a 3
0
-end generated by
resection of the 5
0
strand of the duplex.
57
In the event of a DSB by ionizing
radiation (IR) or chemical agents, the terminal nucleotides are often modified
structurally or exist as protein-bound entities.
58-60
Such modifications pose an
obstacle for downstream repair pathways and are effectively removed by
nucleases and proteases or both.