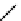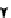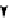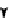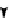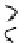Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
3
¢
3
¢
DNA damage
5
¢
-3
¢
Resection
3
¢
3
¢
D-loop formation
DNA synthesis
Sec
ond-e
nd capture
DNA
s
y
nthesis
Double Holliday junction formation
Double HJ di
ssolution
Double HJ
resolution
+
+
Noncrossover
Crossover
Noncrossover
F
IG
. 1. DNA double-strand break repair (DSBR) by homologous recombination (HR). DSBR
is initiated by D-loop formation (strand invasion) by the 3
0
ssDNA overhang that results from strand
resection. The invading DNA strand primes DNA synthesis. During double Holliday junction
(dHJ) formation, the second-end is captured and the strands are ligated after DNA synthesis.
Branch migration can either dissolve dHJs that result in noncrossover products or stabilize dHJs to
undergo resolution. dHJ resolution can result in either crossover or noncrossover products.
II. DSB Repair in Somatic Cells
Eukaryotes have four main pathways that repair DSBs generated sponta-
neously in somatic cells: HR, nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ), alternative
NHEJ (Alt-NHEJ, also known as microhomology-mediated end-joining,
MMEJ), and single-strand annealing (SSA;
Fig. 2
; Ref.
28
). The pathway of
choice depends on the nature of DSB, the species, cell type, and the cell cycle
stage where the DSB occurs.
29