Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
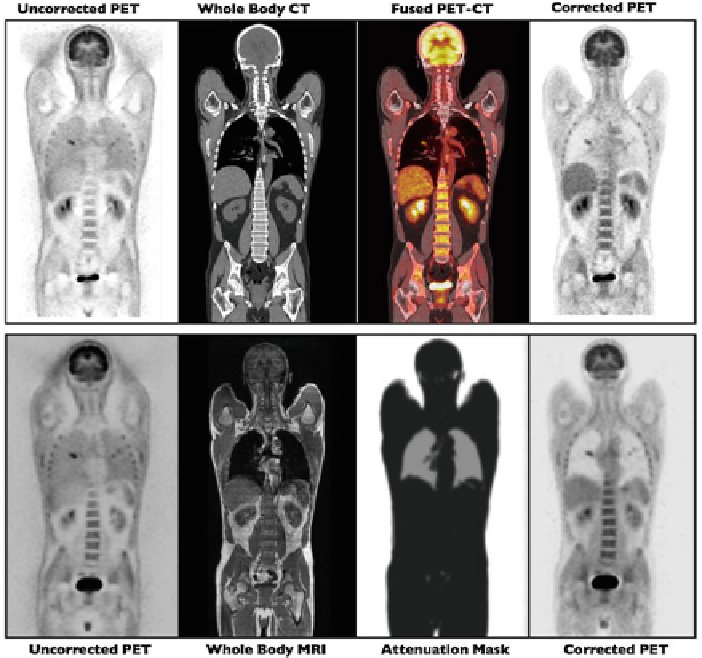
Fig. 3.1
Comparison of CT-guided PET attenuation correction (
upper row
), and MR-guided PET
attenuation correction (
lower row
), obtained in the same patient, where the two hybrid studies were
acquired sequentially
material within the human body, whereas air does not attenuate PET signal at all.
Therefore, MR-based ACmostly uses additional anatomical or spatial information
to predict bone in the attenuation map [
52
]. In the neurological field, it has been
suggested also to use ultrashort-echo-time MRI acquisition techniques rather than
conventional T1-weighted acquisition in order to facilitate the segmentation of the
skulle.g.[
42
,
45
].
•
The segmentation of the lungs, since it has been shown that the density of the
lung tissue is considerably different from subject to subject. Moreover, it depends
on breathing patterns and varies with age that can be up to 30% in the event of
respiratory diseases [
53
,
54
].
•
The segmentation of any other unpredictable benign or malign anatomical abnor-
malities with varying densities [
54
].