Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
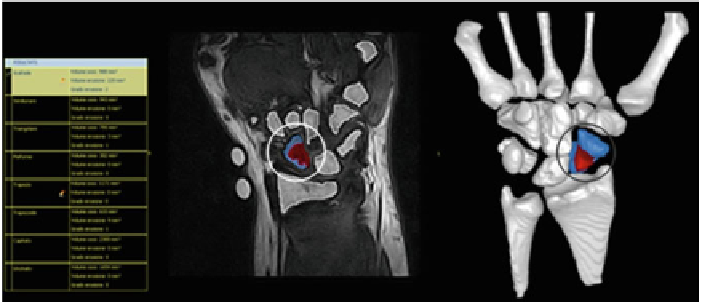
Fig. 12.3
Erosion scoring in the RheumaSCORE software
approach [
41
] has been applied, which does not rely on any prior knowledge of the
shape of healthy bones. Segmentation results are reconstructed in 3D and displayed
using the Marching Cube algorithm [
45
].
After segmentation, the system provides automatic scoring of the bone erosion,
using the samemethod proposed byOMERACTRAMRIS (see Fig.
12.3
). It identifies
and measures bone erosions, defined as the missing volume of substance of the
segmented bone with respect to an average statistical model, which is built on bones
of healthy subjects. Processing takes a few minutes for all wrist bones (or hand
bones), which leads to a substantial reduction of diagnosis time and costs.
A preliminary clinical test has been carried out at DIMI.
1
Twenty six patients
(21 women and five men) diagnosed with early RA according to the 1987 ACR cri-
teria were studied. The wrists were imaged in an extremity-dedicated MRI device
(Artoscan C, Esaote, Genova, Italy) using a turbo T1-weighted sequence. Some
experts evaluated the erosion scores using the manual RAMRIS method and the
RheumaSCORE software. The results of this study showed a good correlation
between the RheumaSCORE analysis and the RAMRIS erosion score [
19
].
Moreover, the framework permits the management and storage of clinical data (like
C-reactive protein), useful for measurement and monitoring the disease activity of
RA. Physicians can also add annotations, possibly using the system ontology, in
order to highlight lessons learnt or critical issues linked to specific features of the
current patient.
All the information related to the patient's examination (e.g. acquired DICOM
images, anatomical 3D segmented elements, 3D features, user annotations) are stored
in the system database and are available for retrieval. The patient disease follow-up
is supported by storing, visualizing and comparing several sets of data acquired
at different times. Differences among parameters and trends can be computed and
visualized.
1
DIMI—Dipartimento di Medicina Interna, Clinica Reumatologica, Università degli Studi di
Genova
.