Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
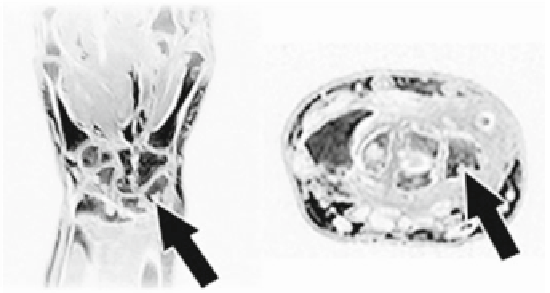
Fig. 12.2
MRI of a wrist affected by RA and with bone erosions. The
white arrows
indicate on the
coronal plane (
left
) and on the axial plane (
right
), the erosion of the triquetral bone
Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common and serious forms of arthritis. It
can lead to long-term joint damage, resulting in chronic pain, loss of function and
disability. This chronic disease affects about 2.9 million people in Europe [
57
,
58
].
An early diagnosis, the continuous monitoring of disease activity and the constant
evaluation of therapy effects can improve patients' quality of life and may reduce
related social costs. Several laboratory tests (e.g. rheumatoid factor, C-reactive pro-
tein) and instrumental exams (e.g. MRI) are available to evaluate RA progression and
joint damage. MRI has been demonstrated to be two to ten times more sensitive than
conventional radiography in detecting wrist erosions in RA (Fig.
12.2
), especially in
its early phases [
59
]. In general, erosions detectable on MRI may become visible
in x-ray images only 2-6years later [
60
-
62
]. This increased sensitivity is explained
by the fact that MRI is a multi-planar technique. Moreover, it can display the soft
tissues, including the synovial membrane, fluid and tendons, in addition to bones and
cartilage. The quantification of synovial volume can be used to monitor the response
to therapy and to predict which patients are more likely to develop erosions within
one year [
63
].
The wide use of MRI in the assessment of joints in RA patients in the last years
emphasizes the need for an objective and reproducible scoring system of RA lesions.
An international working group developed a MRI scoring system to assess both
inflammation (activity) and bone lesions (damage) in RA patients based on the Out-
come Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT) [
64
].
The OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Image Scoring, or
RAMRIS (RA-MRI) Scoring system was developed in order to measure the lesions
observed in the wrist/hand of patients with RA. These lesions comprise
synovitis
(inflammation of the synovial membrane and other typical forms of arthritis),
bone
marrow edema
(inflammation of the bone marrow), and
erosion
(the destructive bone
erosion typical of RA). The erosion score is estimated visually by the user in the tra-
ditional RAMRIS: each eroded bone is considered individually and the ratio between
the volume of the erosion and the hypothetically healthy bone is evaluated, analyzing