Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
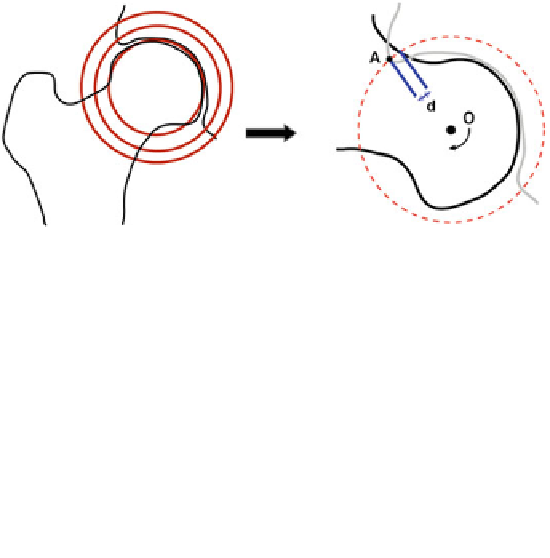
Fig. 8.7
Left
Cylindrical segmentation of the space around the hip joint.
Right
Curvilinear pene-
tration depth obtained by cylindrical segmenting method ('
d
' represents the amount of curvilinear
penetration depth of vertex '
A
' located on the labrum (
light colored
) inside femur bone (
dark
colored
), when the bone is rotating about '
O
') [
13
,
14
,
16
] (With kind permission from Springer
Science+Business Media: Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, Sensitiv-
ity of hip tissues contact evaluation to the methods used for estimating the hip joint center of rotation,
Vol. 50, 2012, pp. 595-604, Arbabi E, Schmid J, Boulic R, Thalmann D, Magnenat-Thalmann N,
Fig.
8.2
)
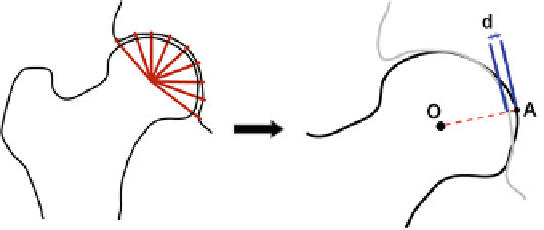
Fig. 8.8
Left
Radial segmentation of the space around the hip joint.
Right
Radial penetration depth
obtained by radial segmentingmethod. '
d
' represents the amount of radial penetration depth of vertex
'
A
' located on the femur cartilage (
dark colored
) inside acetabular cartilage (
light colored
), when
the bone is rotating about '
O
')[
13
,
14
,
16
] (With kind permission from Springer Science+Business
Media: Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, Sensitivity of hip tissues
contact evaluation to the methods used for estimating the hip joint center of rotation, Vol. 50, 2012,
pp. 595-604, Arbabi E, Schmid J, Boulic R, Thalmann D, Magnenat-Thalmann N, Fig.
8.2
)
8.5.3 Evaluation
Ten healthy female subjects (average age: 24) were selected byMIRALab, University
of Geneva for the study. A subject's hip meshes have been simulated by rotating the
hip about five different HJCs, and calculating tissues contact penetration depths
(curvilinear and radial). These rotations and calculations have been done for all the
subjects (totally 50 simulations).
When the penetration depth for different subjects are investigated separately, it
could be seen that for almost all of the estimatedHJCs, radial penetration depth differs